- Molecular Weight: 139.09
- Molecular Formula: C3H10NO3P
- CAS: 10017-11-5
- Molecular Weight: 93.56
- Molecular Formula: C3H7N. HCl
- CAS: 1026-92-2
- Molecular Weight: 246.25
- Molecular Formula: C14H14O4
- CAS: 10519-88-7
- Molecular Weight: 264.44
- Molecular Formula: C18H20 Si
- CAS: 1067-87-4
- Molecular Weight: 178.17
- Molecular Formula: C7H15O3P
- CAS: 1087-21-4
- Molecular Weight: 246.26
- Molecular Formula: C14H14O4
- CAS: 111247-76-8
- Molecular Weight: 118.15
- Molecular Formula: C4H6O2S
- CAS: 1112-91-0
- Molecular Weight: 166.34
- Molecular Formula: C10H18 Si
- CAS: 1113-12-8
- Molecular Weight: 140.3
- Molecular Formula: C8H16 Si
- CAS: 111-45-5
- Molecular Weight: 102.13
- Molecular Formula: C5H10O2
- CAS: 1118-84-9
- Molecular Weight: 142.15
- Molecular Formula: C7H10O3
- CAS: 121092-93-1
- Molecular Weight: 155.09
- Molecular Formula: C3H10NO4P
- CAS: 123-34-2
- Molecular Weight: 132.16
- Molecular Formula: C6H12O3
- CAS: 123-68-2
- Molecular Weight: 156.23
- Molecular Formula: C9H16O2
- CAS: 13361-32-5
- Molecular Weight: 125.13
- Molecular Formula: C6H7NO2
- CAS: 135544-68-2
- Molecular Weight: 199.16
- Molecular Formula: C8H9NO5
- CAS: 142-19-8
- Molecular Weight: 170.25
- Molecular Formula: C10H18O2
- CAS: 142494-81-3
- Molecular Weight: 430.55
- Molecular Formula: C31H26O2
- CAS: 14593-43-2
- Molecular Weight: 148.20
- Molecular Formula: C10H12O
- CAS: 1469-70-1
- Molecular Weight: 130.1418
- Molecular Formula: C6H10 O3
Introduction

Allyl monomers are compounds with the structural formula H2C=CH-CH2R. Unlike vinyl monomers, these compounds polymerize slowly, yielding only low molecular weight polymers or oligomers. Allyl monomers can be divided into linear alpha-substituted products, such as allylamine and allyl chloride, and branched gamma products, such as allyl alcohol and allyl polyethylene glycol. As the world's leading chemical supplier, BOC Sciences provides high quality and high purity allyl monomers to facilitate customers' polymerization research and production.
Allyl amine (CH2=CH-CH2-NH2), an organic compound, is a colorless liquid with strong taste of burning and ammonia, which represents one of the elementary units in organic chemistry. In unsubstituted allylamine, the two functionalities, the nucleophilic amino group and the free alkene can ideally participate in addition reactions, condensation reactions, nucleophilic substitution reactions, radical reactions, cycloaddition reactions, cross-coupling reactions, and metathesis reactions to achieve various synthetic targets. Hence it has the great synthetic value as pharmaceutical intermediates, agricultural chemicals, dyes, coatings, organic synthesis and resin amendment, and can also be used to fabricate amphoteric polymer.
Allyl chloride (CH2=CH-CH2-Cl) is a kind of organic compounds and colorless transparent flammable liquid, which is insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, petroleum and other organic solvents. Allyl chloride is mainly used as an intermediate for the production of epichlorohydrin, propylene glycol and glycerin, and is also a synthetic raw material for pesticides, medicines, spices and coatings.
Allyl alcohol, also known as 2-allyl 1-alcohol, is an organic compound with chemical formula C3H6O. As a widely used structural unit, allyl alcohols can directly participate in the synthesis reactions without pre-functionalization, effectively reducing the synthesis steps and improving the atomic economy. In recent years, various important carbonyl compounds are obtained by migration rearrangements reactions of allyl alcohols (Fig. 1). It is also an intermediate for the production of glycerol, medicine, pesticides, spices and cosmetics.
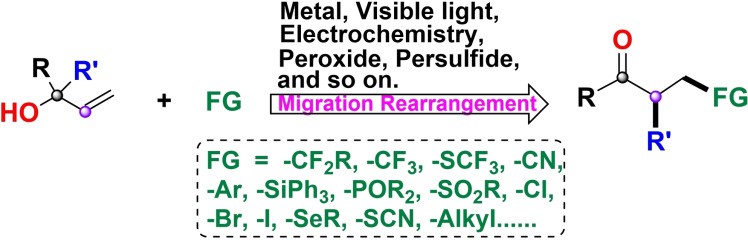 Fig. 1. Examples of allyl alcohol migration reaction (Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis. 2021, 363(16): 3913-3936).
Fig. 1. Examples of allyl alcohol migration reaction (Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis. 2021, 363(16): 3913-3936).
- Allyl Polyethylene Glycol
Allyl polyethylene glycol (APEG, C5H10O2), an important chemical raw material, is formed by the reaction of allyl alcohol and ethylene oxide, which can participate in various chemical reactions ascribing to the molecule contains double bonds, ether bonds, hydroxyl groups. For example, it can be used as a monomer of polymers with double bonds; it can be introduced into the side chain because of the ether bond and hydroxyl bond; as an alcohol, it can be used for the synthesis of esters, especially in the manufacture of fluorine resin soluble in organic solvents. Furthermore, polymeric micelles can be prepared by the copolymerization of allyl polyethylene glycol and N-isopropylacrylamide, which accelerates drug release under acidic conditions and enhance the therapeutic effect (Fig. 2).
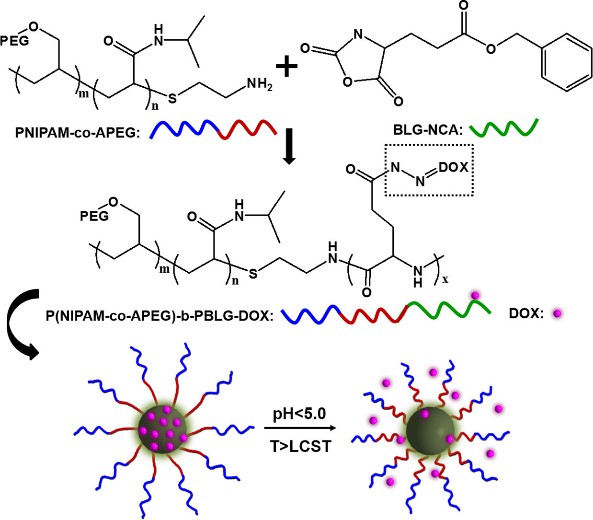 Fig. 2. Preparation and controlled drug release ability of the polymeric micelles (Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2019, 98: 910-917).
Fig. 2. Preparation and controlled drug release ability of the polymeric micelles (Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2019, 98: 910-917).
If you are interested in our allyl monomers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Nag, S. et al. Applications of allylamines for the syntheses of aza-heterocycles. Tetrahedron. 2011, 67(47): 8959-9061.
- Xing, Y. et al. Recent Advances in the Synthetic Use of Migration Reactions of Allyl Alcohols. Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis. 2021, 363(16): 3913-3936.
- Sang, X. et al. Preparation and controlled drug release ability of the poly[N-isopropylacryamide-co-allyl poly(ethylene glycol)]-b-poly(γ-benzyl-l-glutamate) polymeric micelles. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2019, 98: 910-917.





















 Fig. 1. Examples of allyl alcohol migration reaction (Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis. 2021, 363(16): 3913-3936).
Fig. 1. Examples of allyl alcohol migration reaction (Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis. 2021, 363(16): 3913-3936). Fig. 2. Preparation and controlled drug release ability of the polymeric micelles (Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2019, 98: 910-917).
Fig. 2. Preparation and controlled drug release ability of the polymeric micelles (Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2019, 98: 910-917).












