- Molecular Weight: 216.17
- Molecular Formula: C9H13O4P
- CAS: 113-48-4
- Molecular Weight: 275.39
- Molecular Formula: C17H25NO2
- CAS: 1200-88-0
- Molecular Weight: 182.17
- Molecular Formula: C9H10O4
- CAS: 120-74-1
- Molecular Weight: 138.16
- Molecular Formula: C8H10O2
- CAS: 1234203-45-2
- Molecular Weight: 249.26
- Molecular Formula: 0
- CAS: 128-53-0
- Molecular Weight: 125.13
- Molecular Formula: C6H7NO2
- CAS: 13080-90-5
- Molecular Weight: 110.15
- Molecular Formula: C7H10O
- CAS: 13167-25-4
- Molecular Weight: 276.5
- Molecular Formula: C10H4Cl3NO2
- CAS: 154970-45-3
- Molecular Weight: 194.27
- Molecular Formula: C12H18O2
- CAS: 16219-75-3
- Molecular Weight: 120.19
- Molecular Formula: C9H12
- CAS: 1631-25-0
- Molecular Weight: 179.22
- Molecular Formula: C10H13NO2
- CAS: 1631-26-1
- Molecular Weight: 187.19
- Molecular Formula: C11H9NO2
- CAS: 18401-43-9
- Molecular Weight: 256.41
- Molecular Formula: C13H24O3Si
- CAS: 208-96-8
- Molecular Weight: 152.19
- Molecular Formula: C12H8
- CAS: 21635-90-5
- Molecular Weight: 160.26
- Molecular Formula: C12H16
- CAS: 21715-90-2
- Molecular Weight: 179.17
- Molecular Formula: C9H9NO3
- CAS: 2237928-10-6
- Molecular Weight: 192.34
- Molecular Formula: C14H24
- CAS: 29753-26-2
- Molecular Weight: 188.18
- Molecular Formula: C10H8N2O2
- CAS: 3048-64-4
- Molecular Weight: 120.19
- Molecular Formula: C9H12
- CAS: 3048-65-5
- Molecular Weight: 120.19
- Molecular Formula: C9H12
Introduction
Cycloolefins are constituent monomers of cycloolefin copolymers. Cycloolefins have double-bonded olefins in their structure, which can participate in addition reactions and then undergo polymerization to form macromolecular polymers. Currently, dicyclopentadiene (DCPD) and norbornene (NBE) are the most widely used cycloolefin monomers in industry. All of them exhibit high activity in ring-opening metathesis polymerization due to high ring tension.
Dicyclopentadiene (DCPD) with molecular formula C10H12 exists in dimer form with two spatial structures of α and β, which are bridge isomer and pendant isomer, respectively. In the molecular structure, DCPD is a cyclic diene with activated carbon-carbon double bond and methylene structure, which is easy to react with other compounds to form various derivatives, and also easy to self-polymerize to form polymer. DCPD has high application value in the production of unsaturated resins and fine chemicals, and the industrial application of its downstream products also brings higher economic benefits to the market. Based on its high chemical activity, industrial DCPD has been widely used in the fields of medicine, fuel, pesticide, fragrance, synthetic rubber, fine chemicals and chemical intermediates. For example, dicyclopentadiene (DCP) greatly enhanced the long-term stability of the solidified body by forming highly stable poly (As2S3-r-S-r-DCP) copolymers, exhibiting high compressive strength and low arsenic leaching concentration (Fig. 1).
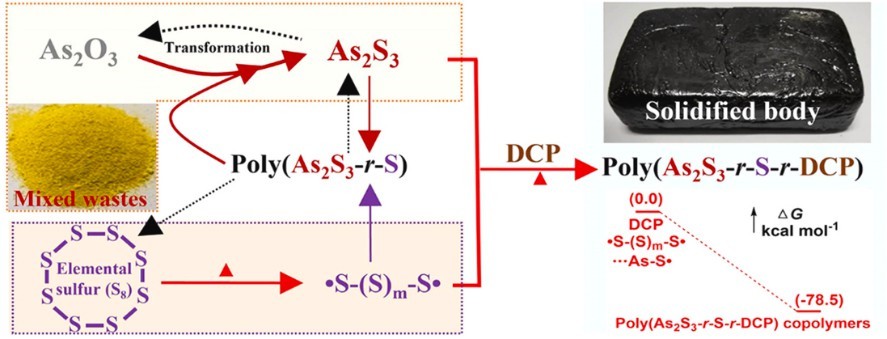 Fig. 1. Preparation and improved compressive strength of the solidified body (Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(10): 1320-1327).
Fig. 1. Preparation and improved compressive strength of the solidified body (Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(10): 1320-1327).
Norbornene is a high value-added product and a raw material for the cycloolefin copolymers synthesis. In industry, ethylene and cyclopentadiene are usually used as raw materials to synthesize norbornene through Diels-Alder reaction. The addition polymerization of norbornene only opens the carbon-carbon double bond and retains the double alicyclic in the monomer, which makes the polymer have excellent heat resistance, low moisture absorption and more chemical resistance. Norbornene has a wide range of applications in the production of optoelectronic materials, special synthetic rubbers, engineering plastics and shape memory materials. In particular, poly-substituted indoles, an important material ubiquitous in medicine, agrochemicals, and organic materials, can be synthesized via the palladium/norbornene synergistic catalysis of oxime esters (Fig. 2).
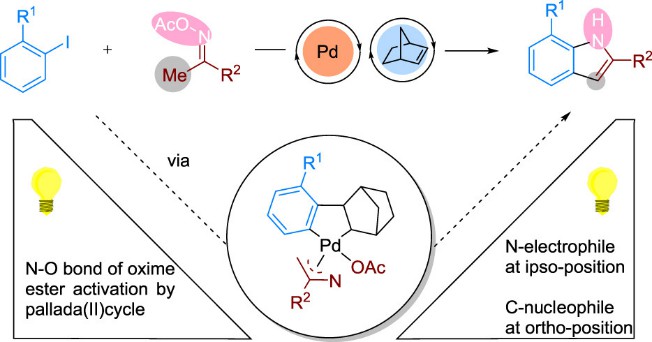 Fig. 2. Preparation of organic materials (Organic Letters. 2022, 24(2): 484-489).
Fig. 2. Preparation of organic materials (Organic Letters. 2022, 24(2): 484-489).
If you are interested in our cycloolefin monomers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Mann, M. et al. Processes for coating surfaces with a copolymer made from sulfur and dicyclopentadiene. Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(10): 1320-1327.
- Kong, L. et al. Chemical solidification/stabilization of arsenic sulfide and oxide mixed wastes using elemental sulfur: Efficiencies, mechanisms and long-term stabilization enhancement by dicyclopentadiene. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2021, 419: 126390.
- Liu, J. et al. Polysubstituted Indole Synthesis via Palladium/Norbornene Cooperative Catalysis of Oxime Esters. Organic Letters. 2022, 24(2): 484-489.


![2'-Hydroxyspiro[norbornene-2,5'- [1,3,2]-dioxaphosphorinane]-2'-oxide](/images/logo.svg)







![tert-Butyl Bicyclo[2.2.1]-5-heptene-2-carboxylate](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/154970-45-3.gif)











 Fig. 1. Preparation and improved compressive strength of the solidified body (Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(10): 1320-1327).
Fig. 1. Preparation and improved compressive strength of the solidified body (Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(10): 1320-1327). Fig. 2. Preparation of organic materials (Organic Letters. 2022, 24(2): 484-489).
Fig. 2. Preparation of organic materials (Organic Letters. 2022, 24(2): 484-489).












