- Molecular Weight: 414.91
- Molecular Formula: C27H24ClP
- CAS: 100-13-0
- Molecular Weight: 149.15
- Molecular Formula: C8H7NO2
- CAS: 100-80-1
- Molecular Weight: 118.18
- Molecular Formula: C9H10
- CAS: 1073-67-2
- Molecular Weight: 138.59418
- Molecular Formula: C8H7Cl
- CAS: 1075-49-6
- Molecular Weight: 148.16
- Molecular Formula: C9H8O2
- CAS: 123333-94-8
- Molecular Weight: 206.19
- Molecular Formula: C8H7NaO3S.xH2O
- CAS: 1255640-65-3
- Molecular Weight: 190.28
- Molecular Formula: C12H18N2
- CAS: 13388-33-5
- Molecular Weight: 234.25
- Molecular Formula: C16H10O2
- CAS: 15016-43-0
- Molecular Weight: 147.97
- Molecular Formula: C8H9O2B
- CAS: 1520-21-4
- Molecular Weight: 119.16
- Molecular Formula: C8H9N
- CAS: 15411-43-5
- Molecular Weight: 119.16
- Molecular Formula: C8H9N
- CAS: 1592-20-7
- Molecular Weight: 152.62
- Molecular Formula: C9H9Cl
- CAS: 1612793-07-3
- Molecular Weight: 330.35
- Molecular Formula: C22H10N4
- CAS: 1712-70-5
- Molecular Weight: 152.62
- Molecular Formula: C9H9Cl
- CAS: 1746-23-2
- Molecular Weight: 160.25
- Molecular Formula: C12H16
- CAS: 18001-13-3
- Molecular Weight: 224.33
- Molecular Formula: C11H16O3Si
- CAS: 2039-82-9
- Molecular Weight: 183.04
- Molecular Formula: C8H7Br
- CAS: 2039-85-2
- Molecular Weight: 138.59
- Molecular Formula: C8H7Cl
- CAS: 2039-86-3
- Molecular Weight: 183.04
- Molecular Formula: C8H7Br
- CAS: 2039-87-4
- Molecular Weight: 138.60
- Molecular Formula: C8H7Cl
Introduction

Styrene monomers are a class of compounds in which benzene rings are connected by ethylene double bonds, and most of them exist in plants, animals and some microorganisms.[1] For many years, the styrene backbone has been recognized as a promising chemical structure, which has excellent application prospects in various fields such as chemical synthesis, biosensing, and organic optoelectronic materials. In addition, styrene monomer shows more excellent development performance in the fields of medical care, light industrial equipment, environmental protection and so on.
Application
Styrene monomers with hydroxyl groups have been shown to have anti-aging and antioxidant effects, inhibit the spread of cancer cells, as well as anti-inflammatory and anti-cardiovascular effects to enhance immunity in the field of nutraceuticals. Styrene derivatives modified with different functional groups have different applications in polymer fields. For example, styrene monomers with acetylene groups can be used as raw materials for liquid crystal displays, styrene derivatives with trifluoromethyl groups can be used as organic nonlinear optical materials, and styrene monomers containing benzoxazole can be used as fluorescent whitening agents in the field of dyes. Furthermore, styrene monomer can significantly improve the bending properties of a novel 3D nanoscale cellulose reinforcement.[2]
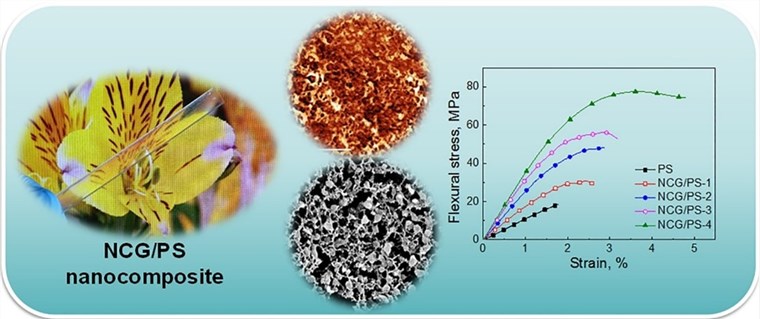 Fig. 1. Preparation of novel 3D nanocellulose reinforcements by polystyrene (Carbohydrate Polymers. 2018, 199: 473-481).
Fig. 1. Preparation of novel 3D nanocellulose reinforcements by polystyrene (Carbohydrate Polymers. 2018, 199: 473-481).
Tetraphenylethylene (TPE) is a typical styrene monomer with a fluorescent light-emitting group and a free-rotating benzene ring propeller-like structure. TPE derivatives are widely used in the synthesis of polymeric materials due to their excellent luminescence properties and easily modified functional groups. In recent years, many important research results have been achieved in the application of TPE derivatives in chemical sensing and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), such as novel light-emitting filaments with significantly improved filament properties.[3]
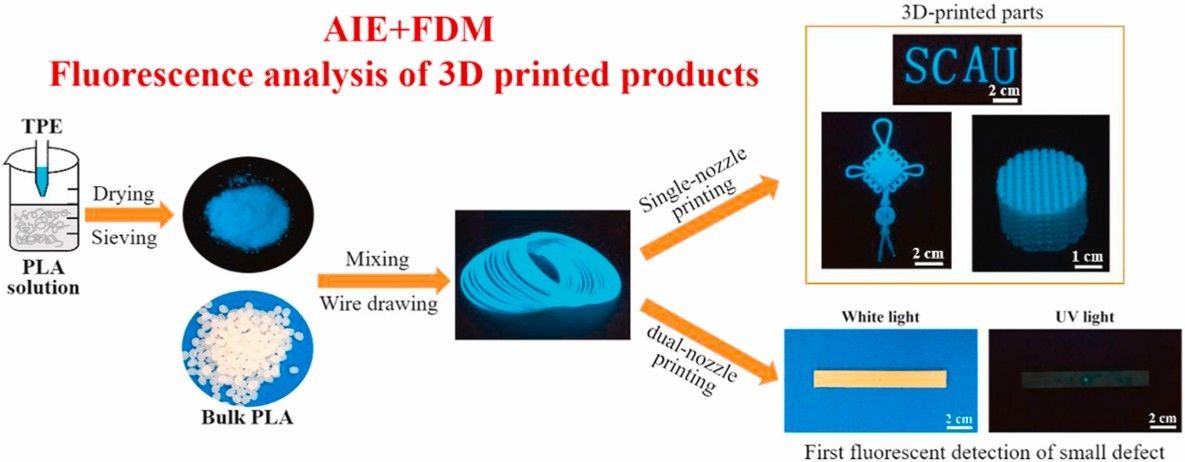 Fig. 2. TPE significantly improves performance of new light-emitting filaments (Composites Part B: Engineering. 2021, 219: 108898).
Fig. 2. TPE significantly improves performance of new light-emitting filaments (Composites Part B: Engineering. 2021, 219: 108898).
If you are interested in our styrenic monomers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Pilevar, Z. et al. Migration of styrene monomer from polystyrene packaging materials into foods: Characterization and safety evaluation. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2019, 91: 248-261.
- Li, K. et al. Mechanically strong polystyrene nanocomposites by peroxide-induced grafting of styrene monomers within nanoporous cellulose gels. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2018, 199: 473-481.
- Yang, F. et al. Novel AIE luminescent tetraphenylethene-doped poly (lactic acid) composites for fused deposition modeling and their application in fluorescent analysis of 3D printed products. Composites Part B: Engineering. 2021, 219: 108898.




















 Fig. 1. Preparation of novel 3D nanocellulose reinforcements by polystyrene (Carbohydrate Polymers. 2018, 199: 473-481).
Fig. 1. Preparation of novel 3D nanocellulose reinforcements by polystyrene (Carbohydrate Polymers. 2018, 199: 473-481). Fig. 2. TPE significantly improves performance of new light-emitting filaments (Composites Part B: Engineering. 2021, 219: 108898).
Fig. 2. TPE significantly improves performance of new light-emitting filaments (Composites Part B: Engineering. 2021, 219: 108898).












