Browse by
Introduction
Biodegradable polymers refer to polymer materials that can be degraded or digested by enzymes in living organisms, and the resulting small molecules can be absorbed by themselves and excreted from the body. Biodegradable polymers are both synthetic and natural and have something in common: all biodegradable polymers are basically stable and durable in their application. Their main chains are mostly composed of aliphatic structural units, which are connected by ester bonds and are easily hydrolyzed. In terms of applications, biodegradable polymers are of great significance in packaging, medical, agricultural and other fields.[1]
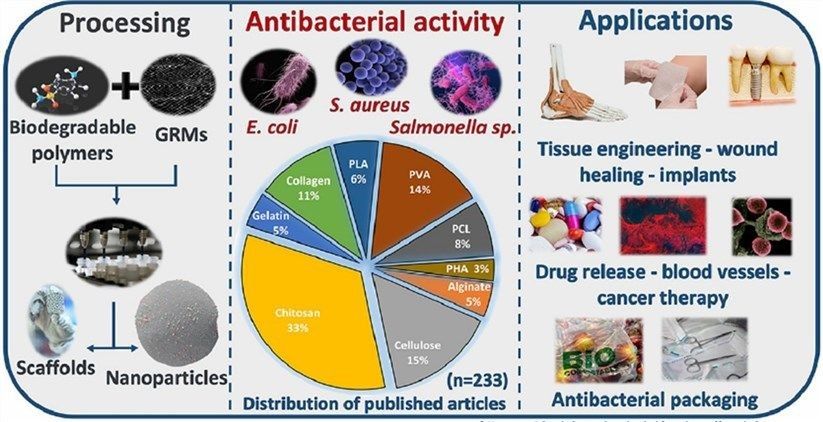 Fig. 1. Biodegradable polymer materials for antibacterial applications (Acta Biomaterialia. 2022, 151: 1-44).
Fig. 1. Biodegradable polymer materials for antibacterial applications (Acta Biomaterialia. 2022, 151: 1-44).
Application
Among all kinds of biodegradable packaging materials, polylactic acid (PLA) has the largest application market, which is recognized as an environmentally friendly material. PLA is a novel biodegradable material made from starch raw materials derived from renewable plant resources such as corn. PLA has excellent biodegradability and can be completely degraded by microorganisms in nature, eventually generating carbon dioxide and water, which is very beneficial to protecting the environment. Currently in industry PLA is mainly used for food packaging and 3D printing. According to the report, food cups made of PLA can be completely degraded in just 60 days, truly achieving the dual effects of ecology and economy.
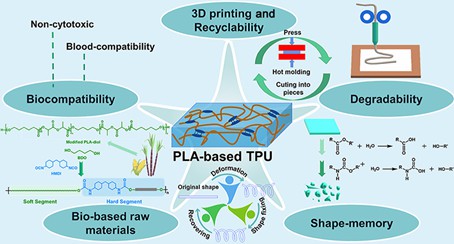 Fig. 2. Application of polylactic acid in 3D printing (Biomacromolecules. 2022, 23(10): 4192-4202).
Fig. 2. Application of polylactic acid in 3D printing (Biomacromolecules. 2022, 23(10): 4192-4202).
Biodegradable polymers have many uses in the medical field, especially in tissue engineering and drug delivery. The advantage of biodegradable polymer materials as a drug delivery system carrier is that the drug can be released to a specific part of the body with the maximum load, then degraded into non-toxic substances, and finally excreted from the body through its own metabolism. During this time, the polymer slowly degrades into smaller molecules, releasing natural products and having the ability to control drug release. Drugs are encapsulated in polymers designed to reduce their toxicity to healthy cells. For example, biodegradable polylactic acid and caprolactone have been used to deliver anticancer drugs.[2]
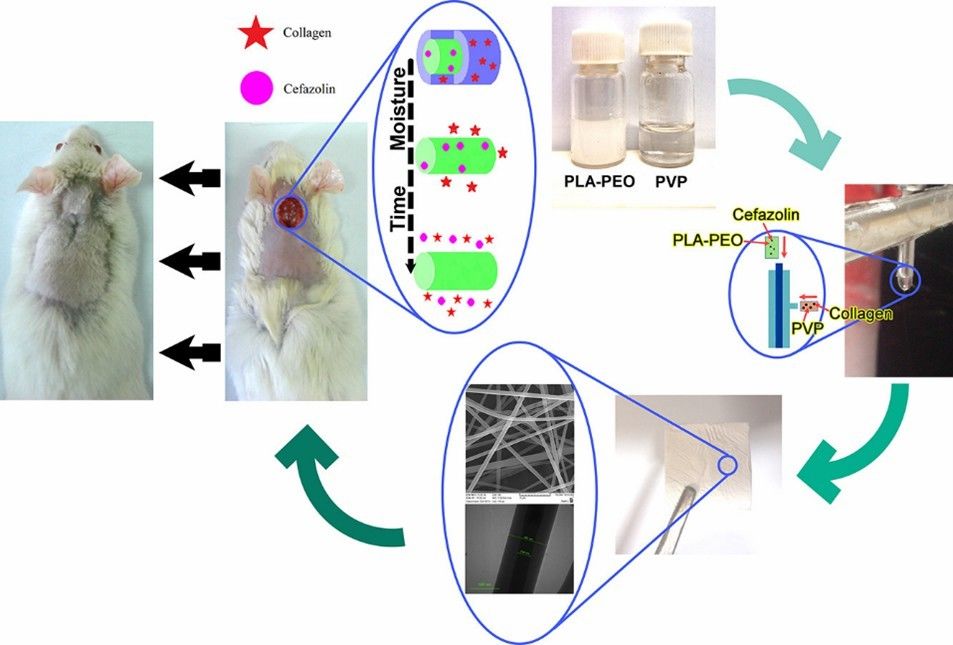 Fig. 3. Application of polylactic acid (PLA) based electrospun nanofibers (International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2021, 172: 143-153).
Fig. 3. Application of polylactic acid (PLA) based electrospun nanofibers (International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2021, 172: 143-153).
Biodegradable polymer materials are also widely used in agriculture. The use of hydrophobic or hydrophilic polymers as the seed appearance effect of bread can reduce or increase the water absorption capacity of seeds to protect the seeds from pests. Commonly used seed coating materials are polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyvinyl alcohol (PVC), etc.
Biodegradable polymer materials have a very broad development prospect and play a huge role in reducing environmental pollution because of their unique properties. In the future, the development and research of biodegradable polymer materials should focus on the polymer varieties that are competitive in terms of basic properties, molding performance and price. If you are interested in our biodegradable polymers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Avcu, E. et al. Biodegradable Polymer Matrix Composites Containing Graphene-Related Materials for Antibacterial Applications: A Critical Review. Acta Biomaterialia. 2022, 151: 1-44.
- Hajikhani, M. et al. Fabrication and characterization of mucoadhesive bioplastic patch via coaxial polylactic acid (PLA) based electrospun nanofibers with antimicrobial and wound healing application. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2021, 172: 143-153.


 Biodegradable AB Diblock Copolymers
Biodegradable AB Diblock Copolymers
 Biodegradable ABA Triblock Copolymers
Biodegradable ABA Triblock Copolymers
 Caprolactone Polymers
Caprolactone Polymers
 Lactide and Glycolide Polymers
Lactide and Glycolide Polymers
 Polyanhydrides and Polyesters
Polyanhydrides and Polyesters
 Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
 Polyphosphazenes
Polyphosphazenes
 Fig. 1. Biodegradable polymer materials for antibacterial applications (Acta Biomaterialia. 2022, 151: 1-44).
Fig. 1. Biodegradable polymer materials for antibacterial applications (Acta Biomaterialia. 2022, 151: 1-44). Fig. 2. Application of polylactic acid in 3D printing (Biomacromolecules. 2022, 23(10): 4192-4202).
Fig. 2. Application of polylactic acid in 3D printing (Biomacromolecules. 2022, 23(10): 4192-4202). Fig. 3. Application of polylactic acid (PLA) based electrospun nanofibers (International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2021, 172: 143-153).
Fig. 3. Application of polylactic acid (PLA) based electrospun nanofibers (International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2021, 172: 143-153).











