- CAS: 103-44-6
- Molecular Weight: 156.27
- Molecular Formula: C10H20O
- CAS: 10471-78-0
- Molecular Weight: 111.14176
- Molecular Formula: C6H9NO
- CAS: 10519-87-6
- Molecular Weight: 112.24
- Molecular Formula: C6H12Si
- CAS: 105-38-4
- Molecular Weight: 100.12
- Molecular Formula: C5H8O2
- CAS: 10603-92-6
- Molecular Weight: 166.06
- Molecular Formula: C5H12N.Br
- CAS: 106-86-5
- Molecular Weight: 124.18
- Molecular Formula: C8H12O
- CAS: 1072-63-5
- Molecular Weight: 94.12
- Molecular Formula: C5H6N2
- CAS: 1075-49-6
- Molecular Weight: 148.16
- Molecular Formula: C9H8O2
- CAS: 111-63-7
- Molecular Weight: 310.51
- Molecular Formula: C20H38O2
- CAS: 1121-55-7
- Molecular Weight: 105.14
- Molecular Formula: C7H7N
- CAS: 114123-73-8
- Molecular Weight: 292.5
- Molecular Formula: C21H40
- CAS: 114651-37-5
- Molecular Weight: 170.25
- Molecular Formula: C10H18O2
- CAS: 116-11-0
- Molecular Weight: 72.10572
- Molecular Formula: C4H8O
- CAS: 1184-84-5
- Molecular Weight: 108.12
- Molecular Formula: C2H4O3S
2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6-Decafluoro-6-[(1,2,2-trifluorovinyl)oxy]hexanenitrile (BPM-366300)
- CAS: 120903-40-4
- Molecular Weight: 373.07
- Molecular Formula: C8F13NO
- CAS: 122-67-8
- Molecular Weight: 204.26
- Molecular Formula: C13H16O2
- CAS: 1271-51-8
- Molecular Weight: 212.07
- Molecular Formula: C12H12Fe
- CAS: 13162-05-5
- Molecular Weight: 71.08
- Molecular Formula: C3H5NO
- CAS: 13388-33-5
- Molecular Weight: 234.25
- Molecular Formula: C16H10O2
- CAS: 134072-99-4
- Molecular Weight: 423.80
- Molecular Formula: C15H37NO5Si4
Introduction

Vinyl monomers are excellent chemical raw materials, whose role and status cannot be replaced by other raw materials. The downstream derivatives of vinyl monomers, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are closely related to the national economy and people's lives. At the same time, vinyl monomers, such as propylene, butadiene, benzene, toluene, and xylene, are the basic raw materials for the production of various organic chemical products and synthetic resins, synthetic fibers, and synthetic rubber.
Vinyl chloride is a representative vinyl monomer with the chemical formula C2H3Cl. As an important organic compound, vinyl chloride is an indispensable monomer in the polymer chemical industry. Vinyl chloride is widely used in the manufacture of polyvinyl chloride homopolymers and copolymers, and can also be copolymerized with vinyl acetate, butadiene, etc. Meanwhile, vinyl chloride can also be used as an extractant for dyes and spices. For example, PVC plasticized with cold-resistant bio-based plasticizer synthesized from oleic acid exhibits remarkable migration and cold resistance.[1]
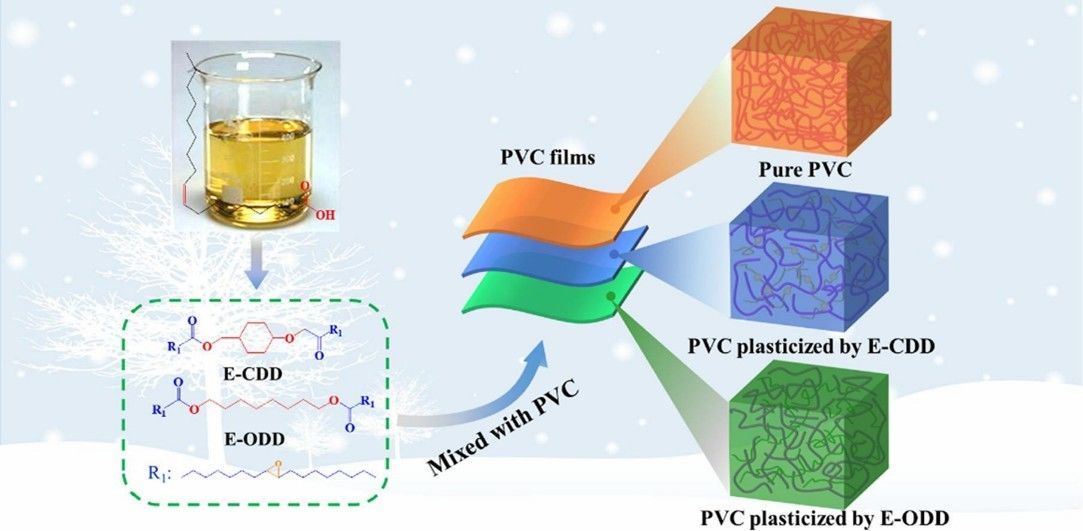 Fig. 1. Preparation of bio-based plasticizer by vinyl chloride (European Polymer Journal. 2021, 142: 110154).
Fig. 1. Preparation of bio-based plasticizer by vinyl chloride (European Polymer Journal. 2021, 142: 110154).
Styrene (C8H8) is an organic compound formed by replacing one hydrogen atom of ethylene with benzene. Due to the electronic conjugation of vinyl and benzene rings, styrene will gradually polymerize and oxidize when exposed to air. As an important monomer, styrene is more and more widely used in synthetic resin, ion exchange resin and synthetic rubber industry.
In addition, propylene monomer is one of the basic raw materials of the three major synthetic materials, the largest use of which is the production of polypropylene. The chemical properties of propylene are determined by its double bond and the hydrogen atoms on the allyl group. Propylene monomers can produce acrylonitrile, propylene oxide, and the like. Various propylene monomer-based materials are used in biomedical applications, including hydrogels for bioprinting, due to their controllable mechanical properties, tunable degradation, and biocompatibility.[2]
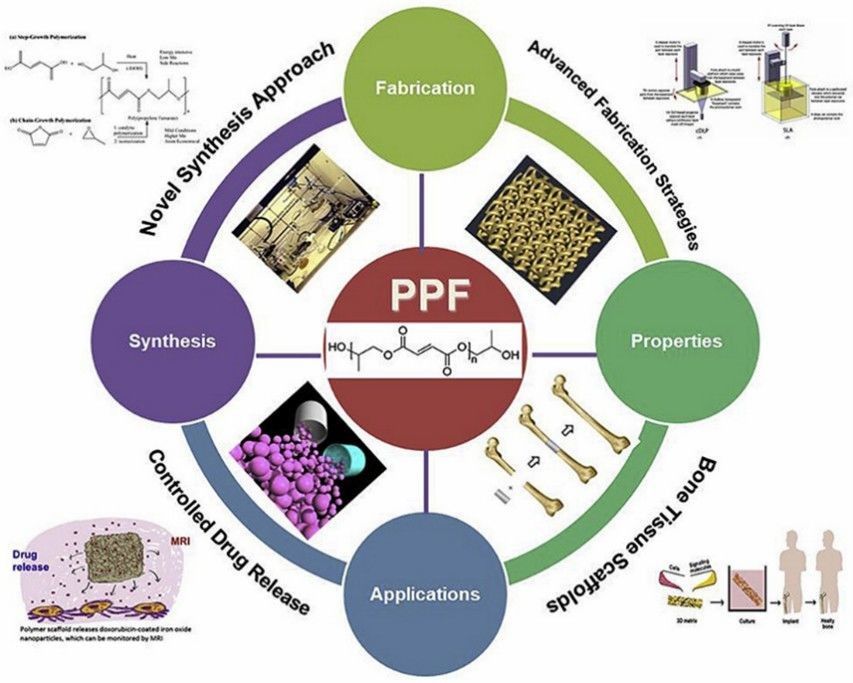 Fig. 2. Biomedical applications of propylene monomers-based materials (Biomaterials. 2019, 208: 45-71).
Fig. 2. Biomedical applications of propylene monomers-based materials (Biomaterials. 2019, 208: 45-71).
In recent years, with the gradual improvement of the polymerization technology and equipment, the development of vinyl monomers has the following characteristics: building a diversified raw material pattern, promoting the lightweight of raw materials, accelerating the upgrading of product structure, and achieving differentiated development. If you are interested in our vinyl monomers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Liu, D. et al. An efficient cold-resistant strategy: Synthesis and application of green cold-resistant bio-based plasticizer for poly(vinyl chloride). European Polymer Journal. 2021, 142: 110154.
- Cai, Z. et al. Poly(propylene fumarate)-based materials: Synthesis, functionalization, properties, device fabrication and biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2019, 208: 45-71.




















 Fig. 1. Preparation of bio-based plasticizer by vinyl chloride (European Polymer Journal. 2021, 142: 110154).
Fig. 1. Preparation of bio-based plasticizer by vinyl chloride (European Polymer Journal. 2021, 142: 110154). Fig. 2. Biomedical applications of propylene monomers-based materials (Biomaterials. 2019, 208: 45-71).
Fig. 2. Biomedical applications of propylene monomers-based materials (Biomaterials. 2019, 208: 45-71).












