- CAS: 26142-30-3
- Molecular Formula: (C3H6O)n.C6H10O3
- CAS: 72207-80-8
- Molecular Formula: C3H5O2-(C2H4O)n-C3H5O
What Are Epoxy Polymers?
Epoxy polymer refers to a high molecular polymer containing two or more epoxy groups and an organic compound such as aliphatic, alicyclic or aromatic as the backbone. Epoxy polymer networks are usually formed by the reaction of polyepoxides (monomers) with polyamines (hardeners), as shown in Figure 1. The resulting crosslinked system forms a rigid network and thus can form mechanically durable materials. Epoxy polymers have very interesting physicochemical properties. To further develop new materials, their properties (thermal, mechanical, flame retardant, electrical, dielectric, corrosion protection, viscosity, viscoelasticity, rheology, etc.) can be improved by chemical modification.
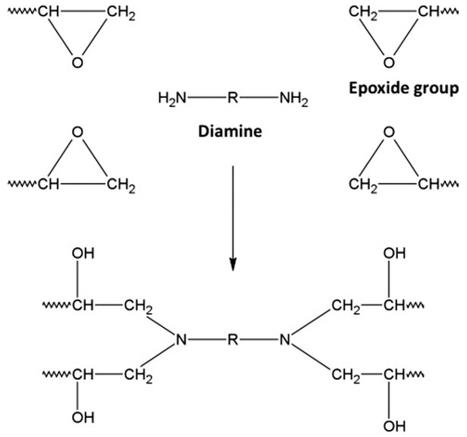 Fig.1 Crosslinking process of a diepoxide/diamine system for an epoxy polymer.[1]
Fig.1 Crosslinking process of a diepoxide/diamine system for an epoxy polymer.[1]
Our epoxy polymers include poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether and polypropylene glycol diglycidyl ether.
- Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether
Polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether is an aliphatic diepoxy resin. It has a wide range of uses, not only as a cross-linking agent, reactive diluent, fabric finishing agent, heat stabilizer and hardening agent for silver halide photographic materials, etc., but also as an intermediate to synthesize different types of Gemini surfactants. High molecular weight polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether can be prepared by using polyethylene glycol, epichlorohydrin and sodium hydroxide as raw materials and tetra-n-butylammonium bromide (TBAB) as phase transfer catalyst.
- Polypropylenglycol diglycidyl ether
The molecular structure of polypropylene glycol diglycidyl ether (PPGDGE) consists of two epoxy resin end groups and repeating ether bond units. PPGDGE can be added to epoxy resin as a reactive diluent to improve its toughness. Polypropylene glycol diglycidyl ether can be synthesized by a two-step process. First, epichlorohydrin and polypropylene glycol undergo a ring-opening reaction under the action of a solid acid catalyst to generate a chlorohydrin ether intermediate. Then the chlorohydrin ether and solid sodium hydroxide undergo a ring-closure reaction under the action of a phase transfer catalyst. PPGDGE can be combined with hydrogen epoxy resin and maleic anhydride to prepare shape memory materials.
Applications of Epoxy Polymers
Epoxy polymers are widely used in coatings, electronics, aerospace and biomedical fields due to their excellent mechanical properties, high adhesive strength, good heat resistance, and high electrical resistance. Different polymer types, curing agents and curing processes can affect the range of applications for epoxy polymers.
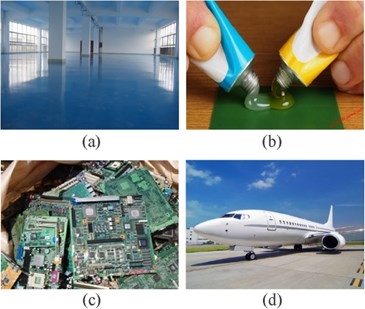 Fig.2 Photos of epoxy resins used in (a) paints and coatings, (b) adhesives, (c) electronic materials, and (d) aerospace industry.[3]
Fig.2 Photos of epoxy resins used in (a) paints and coatings, (b) adhesives, (c) electronic materials, and (d) aerospace industry.[3]
Epoxy polymers are widely used in anti-corrosion coatings, high performance and decorative flooring applications based on ease of processing, high safety, excellent solvent and chemical resistance, and excellent adhesion to many substrates.
Epoxy polymer systems are used in industrial tooling applications to produce molds, master patterns, laminates, castings, fixtures and other industrial production aids.
Epoxy resins are also widely used in biomedical applications. For example, collagen-based materials have been used in human clinical applications as wound dressings, vascular grafts, and aortic heart valves. Composites composed of epoxy polymers and nanodiamonds have been widely used in biomedical systems due to their excellent properties.
If you are interested in our epoxy polymer products, please contact us immediately!
References
- G. M. Odegard and A. Bandyopadhyay. Physical aging of epoxy polymers and their composites. Jouanal of Polymer Science Part B Polymer Physics. 2011.
- Liu Xiaolong, et al. Mechanical Properties and Curing Kinetics of Epoxy Resin Modified by Polypropylene Glycol Diglycidyl Ether. Engineering Plastics Application. 2021.
- Fan-Long Jin, et al. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 2015, 29:1-11.




 Fig.1 Crosslinking process of a diepoxide/diamine system for an epoxy polymer.[1]
Fig.1 Crosslinking process of a diepoxide/diamine system for an epoxy polymer.[1] Fig.2 Photos of epoxy resins used in (a) paints and coatings, (b) adhesives, (c) electronic materials, and (d) aerospace industry.[3]
Fig.2 Photos of epoxy resins used in (a) paints and coatings, (b) adhesives, (c) electronic materials, and (d) aerospace industry.[3]












