Amine Functional Polymers & Salts
- CAS: 24991-53-5
- Molecular Formula: (C2H4O)n.C4H12N2O
- CAS: 25086-42-4
- Molecular Formula: C8H9N
- CAS: 25322-63-8
- Molecular Formula: (C6H11NO)n
- CAS: 26336-38-9
- Molecular Weight: 43.0678
- Molecular Formula: C2 H5 N
- CAS: 29471-77-0
- Molecular Formula: (C8H10BrN)n
- CAS: 30551-89-4
- Molecular Weight: 15000
- Molecular Formula: C3H7NC3H7NC3H7N
- CAS: 9012-76-4
- Molecular Weight: 60-120 kDa
- Molecular Formula: [C7H15NO4]n
Introduction

Amine functional polymers refer to high molecular amines linked with amino groups on the polymer skeleton, which is nitrated by aliphatic or aromatic organic compounds, introduced with a nitro group and then reduced to obtain an amino polymer. Amino group can react with carbonyl compound to form amides, with halogenated hydrocarbons to form quaternary ammonium, and with nitrites to form diazotization, in which the nitrogen atom in amino group also has coordination ability.
Ammonium salts are ionic compounds composed of ammonium ions and acid ions, usually obtained by the reaction of ammonia and acid. Ammonium salts are generally colorless crystals, easily soluble in water, and have strong bactericidal and insect repellent properties. For example, dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride (DDBAC) can be applied as leveling agents for acrylic fibers and antibacterial agents, where the inhibitory effect and mitigation strategies of DDBAC on anaerobic digestion are enhanced.[1] The quaternary ammonium salt molecules with long-chain alkyl groups have excellent softening effect on various fibers, and can make fibers swell and soften to obtain beautiful and smooth appearance. In addition, quaternary ammonium salts can efficiently remove nitrogen compounds from oil products by forming deep eutectic solvents (DESs).[2] Furthermore, bis-octyl dimethyl ammonium bromide is not only a fungicide, but also has significant softening effect on cotton, wool and synthetic fiber fabrics.
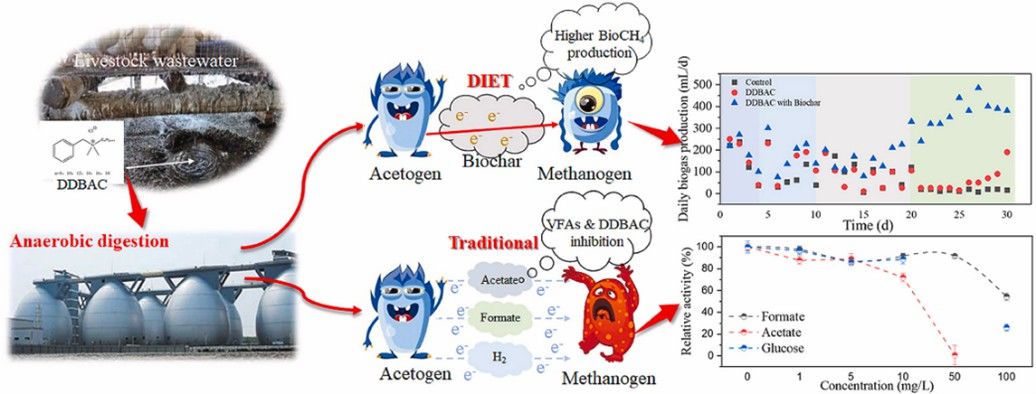 Fig. 1. Biochar assisted cellulose anaerobic digestion under the inhibition of DDBAC (Journal of Environmental Management. 2022, 312: 114934).
Fig. 1. Biochar assisted cellulose anaerobic digestion under the inhibition of DDBAC (Journal of Environmental Management. 2022, 312: 114934).
Polyvinyl amines are common high molecular amines, which can react with carbonyl compounds to introduce functional small molecules by amide bonds. Macromolecular amines are also important carboxyl protection reagents, among which macromolecular amines linked with ester and ether bonds are utilized to protect carboxyl groups in the alkylation reaction of amino acids, or protect carbonyl groups in the methylation reaction of cyclohexanone alpha. Polymeric amines are used to react with other acyl-containing compounds to form amide or urea structures.[3]
If you are interested in our amine functional polymers and salts, please contact us immediately!
References
- Zhao, S. et al. Biochar assisted cellulose anaerobic digestion under the inhibition of dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride: Dose-response kinetic assays, performance variation, potential promotion mechanisms. Journal of Environmental Management. 2022, 312: 114934.
- Qu, Y. et al. Removal intensification of basic and non-basic nitrides from liquid fuels by the optimization design of quaternary ammonium salt green solvents. Fuel. 2022, 326: 125093.
- Chaudhari, S. et al. Surface-modified halloysite nanotube-embedded polyvinyl alcohol/polyvinyl amine blended membranes for pervaporation dehydration of water/isopropanol mixtures. Applied Surface Science. 2019, 493: 193-201.















 Fig. 1. Biochar assisted cellulose anaerobic digestion under the inhibition of DDBAC (Journal of Environmental Management. 2022, 312: 114934).
Fig. 1. Biochar assisted cellulose anaerobic digestion under the inhibition of DDBAC (Journal of Environmental Management. 2022, 312: 114934).











