- CAS: 25067-59-8
- Molecular Weight: average: 90.000
- Molecular Formula: (C12H8NCH:CH2)n
- CAS: 25085-53-4
- Molecular Formula: H[CH(CH3)CH2]nH
- CAS: 25232-41-1
- Molecular Weight: 105.13700
- Molecular Formula: (C7H7N)x
- CAS: 25322-69-4
- Molecular Weight: 134.17
- Molecular Formula: 25322-69-4
- CAS: 25655-35-0
- Molecular Weight: 152.15
- Molecular Formula: C8H8O3
- CAS: 26336-38-9
- Molecular Weight: 43.0678
- Molecular Formula: C2 H5 N
- CAS: 28408-65-3
- Molecular Weight: 85.1045
- Molecular Formula: C4H7NO
- CAS: 29471-77-0
- Molecular Formula: (C8H10BrN)n
- CAS: 30551-89-4
- Molecular Weight: 15000
- Molecular Formula: C3H7NC3H7NC3H7N
- CAS: 49553-93-7
- Molecular Weight: 43.07
- Molecular Formula: C2H5NC2H5NC2H5N
- CAS: 68441-17-8
- Molecular Formula: (-CH2CH2O-)n
- CAS: 82063-35-2
- Molecular Weight: >200.000
- CAS: 9002-89-5
- Molecular Formula: [-CH2CHOH-]n
- CAS: 9002-97-5
- Molecular Weight: 130.09800
- Molecular Formula: C2H3NaO3S
- CAS: 9003-07-0
- Molecular Formula: (C3H6)n
Introduction

Alkene polymers are the largest consumption of synthetic resins. Currently, the global annual consumption has exceeded 100 million tons, and the demand for alkene polymer materials will continue to grow. Alkene polymers are widely used in daily life, industry, agriculture, military and many other fields due to their good performance and low price. Alkene polymers are a class of thermoplastic resins obtained by the separate polymerization or copolymerization of α-olefins such as ethylene, propylene, 1-butene, 1-pentene, 1-hexene, 1-octene, 4-methyl-1-pentene and some cyclic alkene.[1] Due to abundant raw materials, low price, easy processing and molding, and excellent comprehensive properties, alkene polymers are the polymer materials with the largest output and wide application. Among them, polyethylene and polypropylene are the most important, including ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, ethylene-acrylic acid or acrylate copolymers, polypropylene, propylene copolymers, poly(1-butene), poly(4-methyl-1-pentene), cycloolefin polymers.[2]
Other alkene polymers with smaller yields, such as poly(1-butene) polymers, are mainly prepared by gas phase polymerization. Alkene polymers can be extruded, blow molded and injected into pipes, sheets, films and fibers due to their excellent creep resistance and stress crack resistance.[3] For example, poly(4-methyl-1-pentene, 4-methyl-1-pentene) prepared by directional polymerization is the lightest polymer with high transparency, good insulation, corrosion resistance and high breathability (10 times that of polyethylene). Poly(4-methyl-1-pentene, 4-methyl-1-pentene) can be used in the manufacture of optical instruments, medical devices, insulating materials, gas separation membranes and packaging materials, etc.
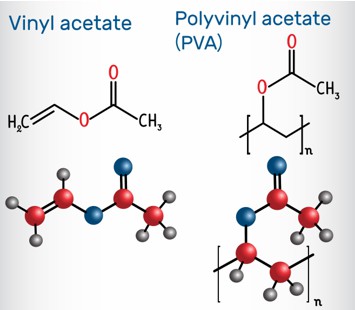 Fig. 1. Examples of vinyl polymers.
Fig. 1. Examples of vinyl polymers.
Vinyl polymers are obtained by the polymerization of vinyl-containing monomers. Typically, vinyl polymers include a wide variety of homopolymers including polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, polyvinyl acetate, polyvinyl alcohol, and poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate), vinyl chloride-ethylene and other copolymers.[4] Among them, Polyethylene, also known as PE, is a thermoplastic resin prepared by the ethylene polymerization. Polyethylene can be processed by conventional thermoplastic molding methods, which has a wide range of uses, such as films, containers, pipes, monofilaments, wires and cables, daily necessities, etc. In addition, polypropylene is also a thermoplastic synthetic resin with excellent properties, which has the advantages of low specific gravity, non-toxicity, easy processing, impact resistance, bending resistance, and good electrical insulation. Polypropylene is widely used in the automotive industry, household appliances, electronics, packaging and building materials and furniture.
Functionalization of alkene and vinyl copolymers is a very valuable research direction. With the continuous development of science and technology, synthesis methods and applications are also constantly innovating to meet the growing demand for such polymers in the chemical industry. If you are interested in our alkene and vinyl polymers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Xiang, M. et al. Progress in Research of Metallocene Catalyst and Olefin Polymer. China Plastics Industry. 2003.
- Guang, Z.B. et al. Synthesis of new phosphine imine ligands and their effects on the thermal stability of late-transition-metal olefin polymerization catalysts. Organometallics. 2002, (17): 21.
- Kotaro, S. et al. Sustainable cycloolefin polymer from pine tree oil for optoelectronics material: living cationic polymerization of beta-pinene and catalytic hydrogenation of high- molecular- weight hydrogenated poly(beta-pinene). Polym Chem-UK. 2014.
- Wang, G.J. et al. Study of Interpenetrating Polymer Network Coating from Acrylic Polyurethane and Vinyl Polymers. Journal of Bulding Materials. 1998.





















 Fig. 1. Examples of vinyl polymers.
Fig. 1. Examples of vinyl polymers.












