- Molecular Weight: 326.4
- Molecular Formula: C20H22O4
- CAS: 1025-15-6
- Molecular Weight: 249.27
- Molecular Formula: C12H15N3O3
- CAS: 1044764-71-7
- Molecular Weight: 314.4
- Molecular Formula: C19H22O4
- CAS: 105-06-6
- Molecular Weight: 130.1864
- Molecular Formula: C10H10
- CAS: 106100-55-4
- Molecular Weight: 456.57114
- Molecular Formula: C27H36O6
- CAS: 1071466-61-9
- Molecular Weight: 392.49
- Molecular Formula: C25H28O4
- CAS: 112309-98-5
- Molecular Weight: 294.39
- Molecular Formula: C20H22O2
- CAS: 1321-74-0
- Molecular Weight: 130.1864
- Molecular Formula: C10H10
- CAS: 26570-48-9
- Molecular Formula: (C3H3O).(C2H4O)n.(C3H3O2)
- CAS: 30499-70-8
- Molecular Formula: (C6H14O3.C3H5ClO)x
- CAS: 30599-15-6
- Molecular Weight: 312.36
- Molecular Formula: C[CH2(OCH2CH2)nOH]4
- CAS: 31694-55-0
- Molecular Weight: 224.25
- Molecular Formula: HO(CH2CH2O)nCH[CH2(OCH2CH2)nOH]2
- CAS: 3454-29-3
- Molecular Weight: 302.36
- Molecular Formula: C15H26O6
- CAS: 35288-49-4
- Molecular Weight: 255.09672
- Molecular Formula: C12H8Cl2O2
- CAS: 36837-97-5
- Molecular Weight: 290.40
- Molecular Formula: C12H18O4S2
- CAS: 39423-51-3
- Molecular Weight: average Mn 440
- Molecular Formula: C2H5C[CH2[OCH2CH(CH3)]nNH2]3
- CAS: 40039-93-8
- Molecular Weight: 636.4
- Molecular Formula: C18H17Br4ClO3
- CAS: 50586-59-9
- Molecular Weight: 266.33
- Molecular Formula: (C2H4O)n(C2H4O)n(C2H4O)nC6H14O3
- CAS: 51258-15-2
- Molecular Weight: 230.25600
- Molecular Formula: HO(C3H6O)x(CH2CH2O)yCH[CH2(OCH2CH2)y(OC3H6)xOH]2
Introduction

Crosslinking reagents (or crosslinkers) are molecules that contain two or more reactive ends capable or chemically attaching to specific functional groups on polymer molecules. Crosslinking agent is an important part of light hydrocarbon resist, in which the photochemical curing effect of photoresist depends on the reaction of the crosslinking agent with dual photosensitive functional groups.
Types of Crosslinking Reagents
Organic peroxide crosslinkers are easily decomposed by light or heat to produce free radicals, which can initiate crosslinking reactions. Organic peroxide is widely used as a crosslinking agent for styrene-butadiene rubber (SPBR) and cis-butadiene rubber (BR) by improving the weather resistance, heat resistance and cold resistance of rubber. Dicumyl peroxide (DCP) is a representative of this class of crosslinking agents with strong oxidizing power and is widely used in the production of various polymer products, including natural gums, synthetic gums and polyethylene resins. The addition of dicumyl peroxide resulted in enhanced heat resistance, mechanical properties and antioxidant properties of the synthetic material. For example, adding a certain amount of DCP crosslinking agent in the preparation of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) composites can obtain polymer materials with excellent water/thermal dual-responsive shape memory properties (Fig. 1).
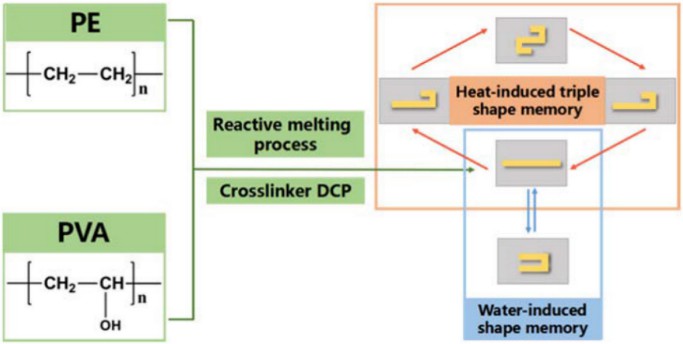 Fig. 1. Preparation of PVA composite material by organic peroxide crosslinkers (Polymer. 2018, 146: 267-274).
Fig. 1. Preparation of PVA composite material by organic peroxide crosslinkers (Polymer. 2018, 146: 267-274).
Amine has been widely used as crosslinking agents for halogen polymers and carbonyl polymers. It is characterized by the crosslinking of epoxy resins at room temperature, fast crosslinking speed, and release of a large amount of heat, especially in the curing of epoxy resins and polyurethane rubber. Mechanistically, the crosslinking agent is exposed during the crosslinking process to generate diradicals, which interact with the resin to form bridge bonds between polymer molecular chains, thereby producing insoluble substances with a three-dimensional structure. For example, triethanolamine (TEOA) has been widely used as a crosslinking agent in graphene oxide, which effectively inhibits the expansion of graphene oxide layered structure with good permeability and selectivity (Fig. 2).
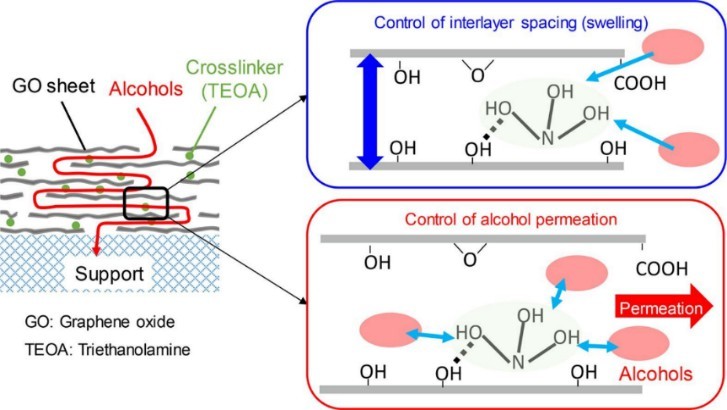 Fig. 2. Preparation of graphene oxide with promising permeation and selective performance (Separation and Purification Technology. 2021, 276: 119279).
Fig. 2. Preparation of graphene oxide with promising permeation and selective performance (Separation and Purification Technology. 2021, 276: 119279).
- Organic Sulfide Crosslinker
Organic sulfides are widely used as crosslinking agents in the rubber industry. They precipitate sulfur at the vulcanization temperature, which makes rubber vulcanized, so they are also known as sulfur donors. Most importantly, the formation of disulfide bond and single sulfur bond in this progress makes vulcanized rubber particularly excellent heat resistance. For example, bio-based polyester elastomers (BPE) can be prepared using reverse vulcanized polysulfides as crosslinking agents, which give crosslinked BPE excellent mechanical properties and ductility and recyclability (Fig. 3).
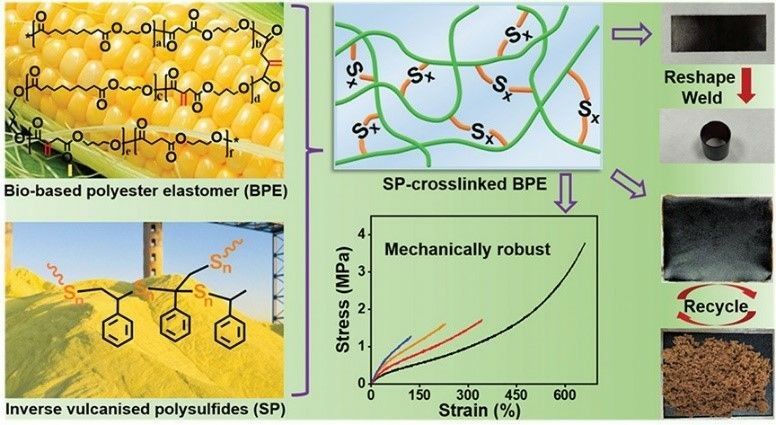 Fig. 3. Preparation of bio-based polyester elastomer using an inverse vulcanized polysulfide as a crosslinker (Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(4): 485-491).
Fig. 3. Preparation of bio-based polyester elastomer using an inverse vulcanized polysulfide as a crosslinker (Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(4): 485-491).
If you are interested in our crosslinking agents, please contact us immediately!
References
- Liu, Y. et al. Fabricating dual-responsive shape memory PVA-based composites via reactive melt-mixing by skillfully utilizing excellent flowability and crosslinking heat of polyethylene. Polymer. 2018, 146: 267-274.
- Nakagawa, K. et al. Controlling interlayer spacing and organic solvent permeation in laminar graphene oxide membranes modified with crosslinker. Separation and Purification Technology. 2021, 276: 119279.
- Wang, D. et al. A bio-based, robust and recyclable thermoset polyester elastomer by using an inverse vulcanised polysulfide as a crosslinker. Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(4): 485-491.



 diacrylate.gif)


















 Fig. 1. Preparation of PVA composite material by organic peroxide crosslinkers (Polymer. 2018, 146: 267-274).
Fig. 1. Preparation of PVA composite material by organic peroxide crosslinkers (Polymer. 2018, 146: 267-274). Fig. 2. Preparation of graphene oxide with promising permeation and selective performance (Separation and Purification Technology. 2021, 276: 119279).
Fig. 2. Preparation of graphene oxide with promising permeation and selective performance (Separation and Purification Technology. 2021, 276: 119279). Fig. 3. Preparation of bio-based polyester elastomer using an inverse vulcanized polysulfide as a crosslinker (Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(4): 485-491).
Fig. 3. Preparation of bio-based polyester elastomer using an inverse vulcanized polysulfide as a crosslinker (Polymer Chemistry. 2022, 13(4): 485-491).












