Dendrimer Building Blocks
- CAS: 10272-07-8
- Molecular Weight: 153.18
- Molecular Formula: C8H11NO2
- CAS: 105309-59-9
- Molecular Weight: 636.01
- Molecular Formula: C25H16Br4
- CAS: 1078153-58-8
- Molecular Weight: 558.54
- Molecular Formula: C34H22O8
- CAS: 129536-41-0
- Molecular Weight: 807.77
- Molecular Formula: C49H43BrO6
- CAS: 143330-91-0
- Molecular Weight: 285.51
- Molecular Formula: C9H7Cl3O4
- CAS: 14615-72-6
- Molecular Weight: 318.37
- Molecular Formula: C21H18O3
- CAS: 152811-37-5
- Molecular Weight: 1047.98
- Molecular Formula: C57H59BrO14
- CAS: 17213-57-9
- Molecular Weight: 200.62
- Molecular Formula: C9H9ClO3
- CAS: 17213-58-0
- Molecular Weight: 181.19
- Molecular Formula: C9H11NO3
- CAS: 173550-33-9
- Molecular Weight: 396.31
- Molecular Formula: C19H12N2O8
- CAS: 176650-92-3
- Molecular Weight: 440.49
- Molecular Formula: C25H28O7
- CAS: 176650-93-4
- Molecular Weight: 503.38
- Molecular Formula: C25H27BrO6
- CAS: 177991-01-4
- Molecular Weight: 416.52
- Molecular Formula: C33H20
- CAS: 17878-23-8
- Molecular Weight: 308.09
- Molecular Formula: C9H12Br2Si
- CAS: 182250-70-0
- Molecular Weight: 616.95
- Molecular Formula: C39H44O3Si2
- CAS: 18226-42-1
- Molecular Weight: 356.88
- Molecular Formula: C9H9Br3
- CAS: 186605-76-5
- Molecular Weight: 538.49944
- Molecular Formula: C28H26O11
- CAS: 195189-45-8
- Molecular Weight: 336.34
- Molecular Formula: C19H16N2O4
- CAS: 2150-37-0
- Molecular Weight: 196.20
- Molecular Formula: C10H12O4
- CAS: 2150-44-9
- Molecular Weight: 168.15
- Molecular Formula: C8H8O4
Introduction
Dendrimer building blocks are macromolecule with dendritic structure, which are composed of the core, polymer main chain and the dendrimer branch chain. Dendrimer building blocks are monodisperse polymers with highly branched structure. The core is centered on the macromolecule and connected with several branched chains, which consist of branched units with terminal outer surface groups.
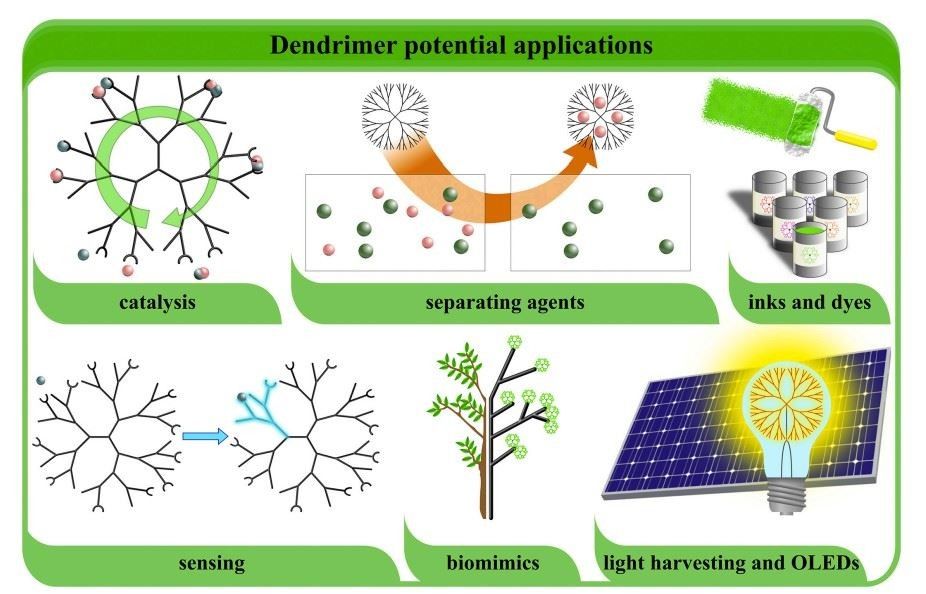 Fig. 1. Schematic representation of dendrimer potential applications (Journal of Controlled Release. 2021, 330: 599-617).
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of dendrimer potential applications (Journal of Controlled Release. 2021, 330: 599-617).
Dendrimer building blocks can be synthesized by divergent synthesis, convergence synthesis and divergence-convergence combination strategy. More than 200 dendrimers have been synthesized, including polyamidoamine (PAMAM), polylysine (L-lysine), polyethylenimine (PEI) and polypropylene imine (PPI), polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyaryl ether nitrile (PEEN), and so on. Dendrimer building blocks are widely used because of their internal cavity structure, abundant active surface functional groups, controllable physical and chemical properties, good hydrodynamic properties, easy film formation and versatility, making them an important class of organic chemicals [1].
Application
Dendrimer building blocks can be widely used in biomedicine, plastic rubber, paint ink, petroleum, nanomaterials, photosensitive materials and water treatment. The applications of dendrimer building blocks are as follows:

- Synthetic Wastewater Treatment Materials
For example, PAMAM as a highly efficient flocculant can effectively treat petroleum wastewater, papermaking and dye wastewater without secondary pollution to the environment. Meanwhile, PAMAM is also a decolorizer with a decolorization rate of more than 98%. PAMAM dendrimer has strong complexing ability with heavy metal ions (Cu2+, Zn2+, and Cr3+), which is suitable for the treatment of tanning wastewater and nuclear industry wastewater.
- Synthetic Self-assembled Monolayer Materials
Dendrimer building blocks are good materials for the preparation of monolayers, colloids, and nanoclusters, and have broad application prospects in the fields of adhesives, chemical sensors, optics, electronics, and thin-film chemistry. Among them, PEEN is widely used in the synthesis of high-performance polymer materials due to its excellent heat resistance and mechanical properties.
- Synthetic Biomedical Materials
Different generations of dendrimers range in diameter from 2 to 10 nanometers, and their natural lumen can accommodate nanoscale metal ions to generate medical nanomaterials. In addition, PEG dendrimers have been widely used in drug delivery, tissue engineering, imaging diagnosis and coupling linkers.
If you are interested in our dendrimer building blocks, please contact us immediately!
Reference
- Buschow, K.H. et al. Dendrimers: polymerization and properties. Science and Technology. 2001, 2042-2052.





![3,5-bis-[3,5-bis-(Benzyloxy)benzyloxy]benzyl bromide](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/129536-41-0.gif)


![3,5-Bis[3,5-bis(3,5-dimethoxybenzyloxy)benzyloxy]benzyl Bromide](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/152811-37-5.gif)







![3,5-BIS[3,5-BIS(METHOXYCARBONYL)PHENOXYMETHYL]PHENOL](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/186605-76-5.gif)



 Fig. 1. Schematic representation of dendrimer potential applications (Journal of Controlled Release. 2021, 330: 599-617).
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of dendrimer potential applications (Journal of Controlled Release. 2021, 330: 599-617).












