- CAS: 24937-79-9
- Molecular Weight: 64.0338
- Molecular Formula: (C2H2F2)x
- CAS: 9002-83-9
- Molecular Weight: 116.47
- Molecular Formula: (C2ClF3)n
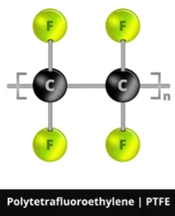
- CAS: 9002-84-0
- Molecular Weight: 100.015612
- Molecular Formula: (C2F4)n
Introduction
Halogenated polymers refer to polymers containing halogen elements such as fluorine, chlorine, and bromine. These elements can be introduced into polymer molecules through substitution or addition reactions. Common halogenated polymers include polytetrafluoroethylene and polyvinyl chloride. The main purpose of halogenation is to improve the performance of materials. For polymers, the most obvious feature is the improvement of flame retardancy. This is because the halogenated polymers will generate free radicals when they decompose, which can effectively capture the free radicals generated by the combustion and degradation of the polymer, thereby inhibiting or terminating the combustion. In addition, inflammable gas will be generated during the combustion process, which can block the contact between the surface of the material and the combustible gas, and further achieve the purpose of flame retardant.
The most studied halogenated polymers are fluorinated, chlorinated and brominated polymers. Fluorinated polymers have strong C-F bonds, resulting in strong chemical inertness, corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance. Common chlorinating reagents include chlorine, sulfonic acid chlorine, hydrogen chloride and hypochlorous acid. The chlorination process is relatively simple, but the corrosion of equipment needs to be considered. The brominated modification is similar to the chlorination method, and the thermal stability of the brominated polymer is better than that of the chlorinated polymer. Common brominated polymers include brominated epoxy resins, polybromophenyl ethers, and bromobutyl rubbers.

Halogenated polymers have the following characteristics:
- High tensile strength
- Strong heat resistance
- Chemically inert
- High flame retardancy
- Low coefficient of friction
- Preservative
- Low conductivity
- High purity
Synthesis of Halogenated Polymers
The synthesis of halogenated polymers can be roughly divided into two ideas, one is obtained by polymerization of halogen-containing monomers; the other is obtained by polymer reaction with halogenating agents. The diagram below presents the different types of halogenated boron-dipyrromethenes.
Application of Halogenated Polymers
A wide variety of halogenated polymer products from BOC Sciences can be used in different industries including: medical, semiconductor, paints, and more.
As a special class of polymer compounds, halogenated polymers are widely used in the medical field. For example, perfluoropolymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene can be used as surgical graft materials such as vascular replacement materials. In addition, such polymers have also performed well in cancer treatment and tissue cell culture.
Halogenation can introduce polar bonds into π-conjugated materials and is an effective strategy to optimize energy levels. Currently, halogenated polymers have been found to be useful as high-efficiency solar cell acceptor materials. It can also be applied to the synthesis of organic semiconductors.
Halogenated polymers can be used as polymer additives to be blended with other polymers to prepare high-performance coatings. For example, blending chlorinated paraffins with polyolefins can produce corrosion-resistant protective coatings with high adhesion and chemical resistance. For another example, coatings obtained by blending chlorinated polypropylene with other resins show excellent adhesion, water resistance, solvent resistance, weather resistance and abrasion resistance.
If you are interested in our halogenated polymer products, please contact us immediately!
Reference
- Vellanki Lakshmi, et al. Halogenated boron-dipyrromethenes: synthesis, properties and applications. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. 2015.




















