- CAS: 100-21-0
- Molecular Weight: 166.13
- Molecular Formula: COOHC6H4COOH
- CAS: 100-21-1
- Molecular Weight: 167
- Molecular Formula: C8H6O5
- CAS: 100-26-5
- Molecular Weight: 167.12
- Molecular Formula: C7H5NO4
- CAS: 10027-07-3
- Molecular Weight: 211.09
- Molecular Formula: C8H12Cl2O2
- CAS: 100-31-2
- Molecular Weight: 268.27
- Molecular Formula: C16H12O4
- CAS: 10443-65-9
- Molecular Weight: 150.96
- Molecular Formula: C3H3BrO2
- CAS: 1076-97-7
- Molecular Weight: 172.18
- Molecular Formula: 0
- CAS: 1078-61-1
- Molecular Weight: 182.17
- Molecular Formula: C9H10O4
- CAS: 109-16-0
- Molecular Weight: 286.32
- Molecular Formula: C14H22O6
- CAS: 110003-22-0
- Molecular Weight: 154.09
- Molecular Formula: C5H5O2F3
- CAS: 110-94-1
- Molecular Weight: 132.11
- Molecular Formula: C5H8O4
- CAS: 111-20-6
- Molecular Weight: 202.25
- Molecular Formula: C10H18O4
- CAS: 1119-62-6
- Molecular Weight: 210.27
- Molecular Formula: C6H10O4S2
- CAS: 1141-38-4
- Molecular Weight: 216.19
- Molecular Formula: C12H8O4
- CAS: 115-28-6
- Molecular Weight: 388.84
- Molecular Formula: C9H4Cl6O4
- CAS: 1171-47-7
- Molecular Weight: 392.25
- Molecular Formula: C17H10F6O4
- CAS: 120-74-1
- Molecular Weight: 138.16
- Molecular Formula: C8H10O2
- CAS: 1215205-10-9
- Molecular Weight: 246.23
- Molecular Formula: C14H11FO3
- CAS: 121-91-5
- Molecular Weight: 166.13
- Molecular Formula: C8H6O4
- CAS: 1293-87-4
- Molecular Weight: 274.05
- Molecular Formula: C12H10FeO4
Introduction
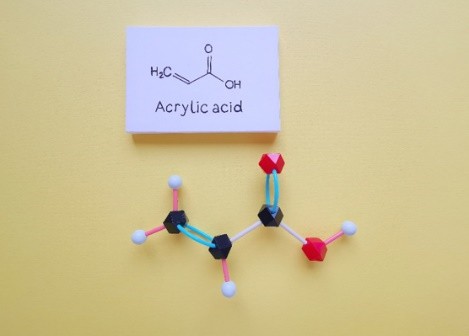
Carboxylic acid is an organic compound with a carboxyl group. Carboxylic acid is a complex functional group consisting of a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group. Carboxylic acids are proton donors, aka protonic acids. Carboxylic acid monomers are high molecular compounds formed by replacing hydrogen atoms in hydrocarbon molecules, which can be divided into aliphatic carboxylic acid monomers, aromatic carboxylic acid monomer and aliphatic cyclic carboxylic acid monomers.
Aliphatic Carboxylic Acid Monomers
- Saturated Carboxylic Acid Monomer: Acetic Acid
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) is an organic monobasic acid and the main component of vinegar. Acetic acid is widely distributed in nature, including fruit or vegetable oils. The dimer formed by acetic acid molecules through hydrogen bonding has high stability. In recent years, acetic acid has been widely used in the production of acetic anhydride, acetate and cellulose acetate as a bulk chemical product. Besides, acetate from low alcohol is an excellent solvent and is widely used in the coatings industry (Fig. 1).
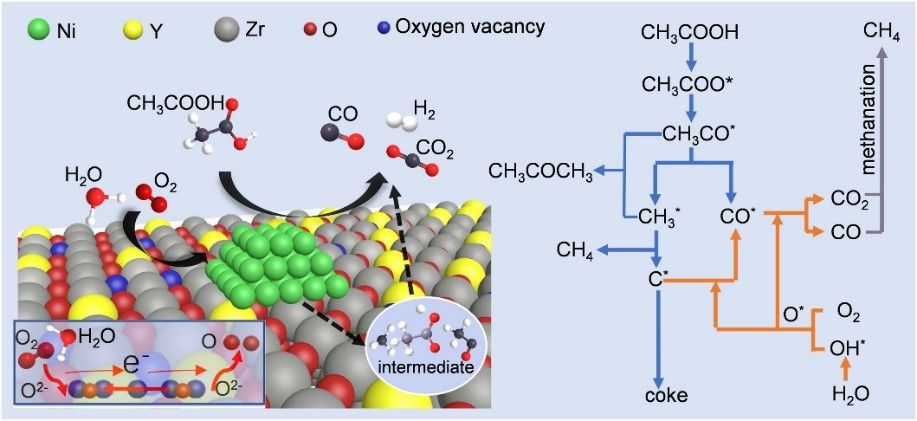 Fig. 1. The evolution route of acetic acid over catalyst in ATR of Hac (Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020, 278: 119264).
Fig. 1. The evolution route of acetic acid over catalyst in ATR of Hac (Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020, 278: 119264).
- Unsaturated Carboxylic Acid Monomer: Trans-Butene Diacid Acid
Trans-butene diacid acid, also known as fumaric acid, is an organic acid that exists widely in nature. Trans-butene diacid acid is generated by the tricarboxylic acid cycle of the organism itself. Trans-butene diacid acid is beneficial for extending the shelf life of powdered products because of its good acidity. Meanwhile, it has significant buffering capacity, gelatinization and antioxidant capacity, and can be used as a raw material to synthesize many high value-added products (Fig. 2). Most importantly, as an additive and regulator in the food processing industry, trans-butene diacid acid plays a vital role in improving taste, antibacterial and mildew resistance.
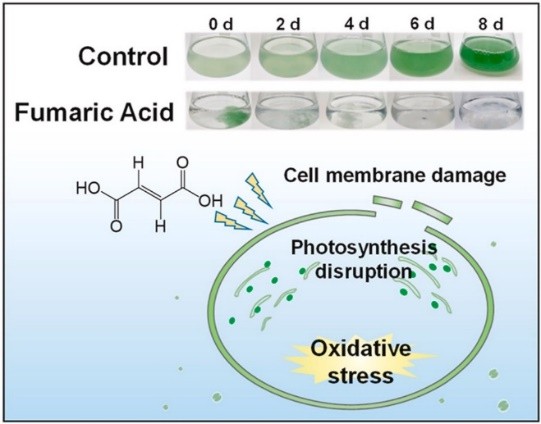 Fig. 2. Preparation of high value-added products by trans-butene diacid (Chemosphere. 2022, 301: 134659).
Fig. 2. Preparation of high value-added products by trans-butene diacid (Chemosphere. 2022, 301: 134659).
- Aromatic Carboxylic Acid Monomer: Benzoic Acid
Benzoic acid is an aromatic acid organic compound with the molecular formula C7H6O2, which is white needle-like or scaly crystals. Benzoic acid is widely found in nature as free acid, ester or its derivatives. Benzoic acid is mainly used in the preparation of sodium benzoate preservatives, but also in synthetic drugs, dyes, plasticizers, mordants, fungicides and fragrances. Furthermore, it may be a promising candidate against drug-resistant pathogens in burn infections (Fig. 3).
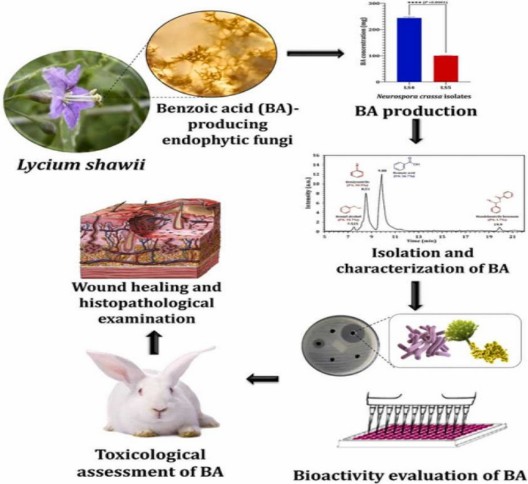 Fig. 3. Preparation of combating drug-resistant pathogens materials (Microbiological Research. 2022, 262: 127108).
Fig. 3. Preparation of combating drug-resistant pathogens materials (Microbiological Research. 2022, 262: 127108).
- Aliphatic Cyclic Carboxylic Acid Monomers: Cyclohexanformic Acid
Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid with chemical formula C7H12O2 is an organic compound that can be catalyzed by the hydrogenation of benzoic acid. As a raw material for organic synthesis, cyclohexanecarboxylic acid can be used in the synthesis of praziquantel for the treatment of anti-pregnancy and schistosomiasis, as well as in the synthesis of organic compounds such as vulcanized rubber compatibilizers, petroleum clarifiers, pesticides, and dyes.
If you are interested in our carboxylic acid monomers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Hu, X. et al. Y-Zr-O solid solution supported Ni-based catalysts for hydrogen production via auto-thermal reforming of acetic acid. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020, 278: 119264.
- Wei, P. et al. Efficient inhibition of cyanobacteria M. aeruginosa growth using commercial food-grade fumaric acid. Chemosphere. 2022, 301: 134659.
- El-Zawawy, N.A. et al. Exploring the potential of benzoic acid derived from the endophytic fungus strain Neurospora crassa SSN01 as a promising antimicrobial agent in wound healing. Microbiological Research. 2022, 262: 127108.






















 Fig. 1. The evolution route of acetic acid over catalyst in ATR of Hac (Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020, 278: 119264).
Fig. 1. The evolution route of acetic acid over catalyst in ATR of Hac (Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020, 278: 119264). Fig. 2. Preparation of high value-added products by trans-butene diacid (Chemosphere. 2022, 301: 134659).
Fig. 2. Preparation of high value-added products by trans-butene diacid (Chemosphere. 2022, 301: 134659). Fig. 3. Preparation of combating drug-resistant pathogens materials (Microbiological Research. 2022, 262: 127108).
Fig. 3. Preparation of combating drug-resistant pathogens materials (Microbiological Research. 2022, 262: 127108).












