Poly(ethylene glycol)s (PEGs) & Derivatives
- CAS: 25322-68-3
- Molecular Formula: H(C2H4O)nOH
Introductions
Polyethylene glycol is a polymer with the chemical formula HO(CH2CH2O)nH, non-irritating, slightly bitter taste, good water solubility, and good compatibility with many organic components. PEG has excellent lubricity, moisture retention, dispersibility and adhesiveness, and can be used as antistatic agent, softener, etc. It is widely used in the fields of cosmetics, medicine, chemical fiber, rubber, plastic, paper, paint, electroplating, pesticide, metal processing industry and food processing industry.

Productions
Polyethylene glycol is produced by the interaction of ethylene oxide with water, ethylene glycol, or ethylene glycol oligomers. The reaction is catalyzed by acidic or basic catalysts. Ethylene glycol and its oligomers are preferred as starting materials instead of water as they allow the production of polymers with low polydispersity (narrow molecular weight distribution). The polymer chain length depends on the ratio of reactants.
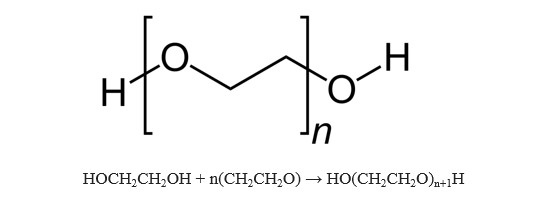
Depending on the catalyst type, the polymerization mechanism can be cationic or anionic. The anionic mechanism is preferred as it allows obtaining PEGs with low polydispersity. The polymerization of ethylene oxide is an exothermic process. Excessive heat or contamination of ethylene oxide with catalysts such as bases or metal oxides can cause runaway polymerization and possible explosion after hours.
Applications
The biological applications of PEG chemistry currently receiving the most attention are as follows:
- PEG-protein conjugates for pharmaceutical applications
- PEG-enzyme conjugates for industrial processing
- Surface modification with PEG to provide protein- and cell-rejecting properties
- Surface modification with PEG to provide control of electroosmosis
- Aqueous two-phase partitioning for protein and cell purification
- PEG hydrogels for cell encapsulation, drug delivery and wound covering
- PEG-modification of small-molecule pharmaceuticals
- PEG tethers for synthesis of biomolecules
- PEG tethering of molecules for biological targeting and signaling
- PEG-liposomes and micelles for drug delivery.
If you are interested in our poly(ethylene glycol)s (PEGs) & derivatives, please contact us immediately!



















