Biodegradable Polymer Monomers
- Molecular Weight: 292.28
- Molecular Formula: (C6H11O5)OCH2CH2OCOC(=CH2)CH3
- CAS: 104-50-7
- Molecular Weight: 142.20
- Molecular Formula: C8H14O2
- CAS: 105-21-5
- Molecular Weight: 128.17
- Molecular Formula: C7H12O2
- CAS: 106-02-5
- Molecular Weight: 240.38
- Molecular Formula: C15H28O2
- CAS: 109-29-5
- Molecular Weight: 254.41
- Molecular Formula: C16H30O2
- CAS: 13076-19-2
- Molecular Weight: 144.13
- Molecular Formula: C6H8O4
- CAS: 1309656-54-9
- Molecular Weight: 168.15
- Molecular Formula: C8H8O4
- CAS: 151078-50-1
- Molecular Weight: 442.46
- Molecular Formula: C24H26O8
- CAS: 177080-66-9
- Molecular Weight: 198.22
- Molecular Formula: C10H14O4
- CAS: 21150-70-9
- Molecular Weight: 200.23
- Molecular Formula: C10H16O4
- CAS: 2235-00-9
- Molecular Weight: 139.19
- Molecular Formula: C8H13NO
- CAS: 3041-16-5
- Molecular Weight: 102.09
- Molecular Formula: C4H6O3
- CAS: 3068-88-0
- Molecular Weight: 86.09
- Molecular Formula: C4H6O2
- CAS: 4511-42-6
- Molecular Weight: 144.13
- Molecular Formula: C6H8O4
- CAS: 502-44-3
- Molecular Weight: 114.14
- Molecular Formula: C6H10O2
- CAS: 502-97-6
- Molecular Weight: 116.07
- Molecular Formula: C4H4O4
- CAS: 532424-75-2
- Molecular Weight: 200.19
- Molecular Formula: C9H12O5
- CAS: 542-28-9
- Molecular Weight: 100.12
- Molecular Formula: C5H8O2
- CAS: 547-65-9
- Molecular Weight: 98.10
- Molecular Formula: C5H6O2
- CAS: 62873-16-9
- Molecular Formula: C6H8O2
Introduction

Chemicals that can undergo polymerization to synthesize biodegradable polymers are called biodegradable polymer monomers. Biodegradable polymer materials can be degraded in vivo to generate small molecules, which have been widely used in biomedical fields such as gene delivery, drug delivery, tissue engineering scaffolds, wound dressings, nanotechnology, wound dressings, and enzyme immobilization. Currently, the most widely used biodegradable monomers mainly include lactic acid, ε-caprolactone and 1,4-butanediol.
Lactic acid is a natural organic acid with a molecular formula of C3H6O3, its molecular structure contains chiral carbon and its configuration is mostly L. Lactic acid has a wide range of sources, and its industrial production is mainly produced by biological fermentation from renewable resources such as corn and sugarcane. Lactic acid is commonly used as a food additive and acid-base regulator in the food industry. Furthermore, lactic acid-derived products are used as preservatives and disinfectants in aquaculture, and their safety performance is superior to traditional preservatives. Lactic acid contains hydroxyl and carbonyl groups, which can be dehydrated and esterified to form a polymer of lactic acid molecules, which is an important source of monomers for the new biodegradable plastic polylactic acid (Fig. 1).
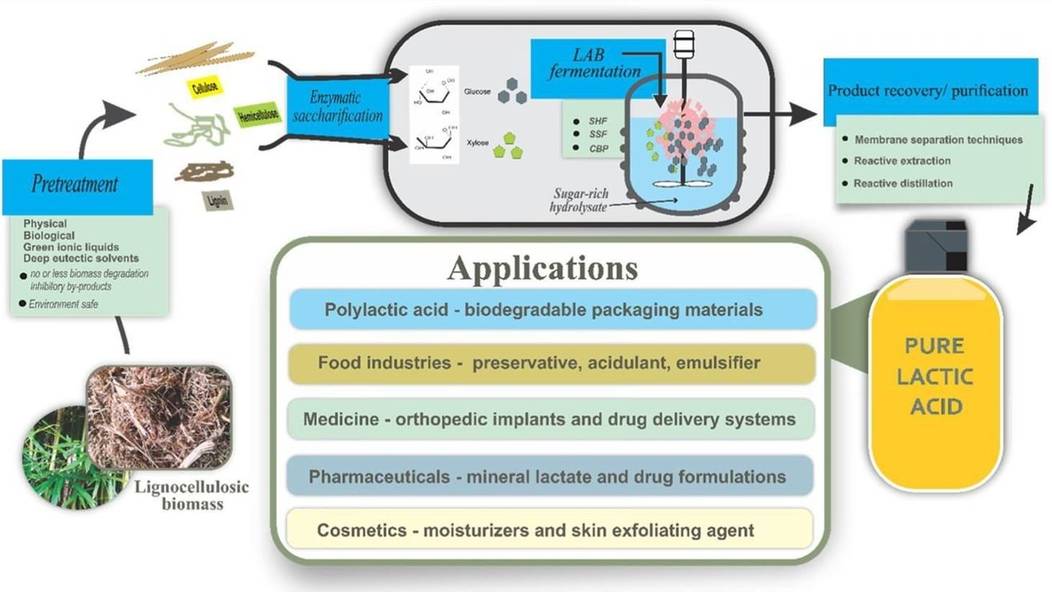 Fig. 1. Preparation and application of pure lactic acid (Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2021, 21: 101337).
Fig. 1. Preparation and application of pure lactic acid (Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2021, 21: 101337).
ε-caprolactone (C6H10O12) is a chemically unstable colorless aromatic oily liquid, easily soluble in water, ethanol and benzene. ε-caprolactone is widely used in biomedicine and environmentally degradable materials due to its excellent biocompatibility and drug permeability. In addition, ε-caprolactone polyols are prepared by ring-opening under the initiation of polyols, and are commonly used raw materials for the synthesis of high-performance polyurethanes. ε-caprolactone can also be used as a modifier, providing excellent chemical properties in compound synthesis. Additionally, caprolactone can be copolymerized with L-lactide, glycolide, and other esters under the initiation of magnesium, zinc, and aluminum complexes to produce high-performance polymer materials (Fig. 2).
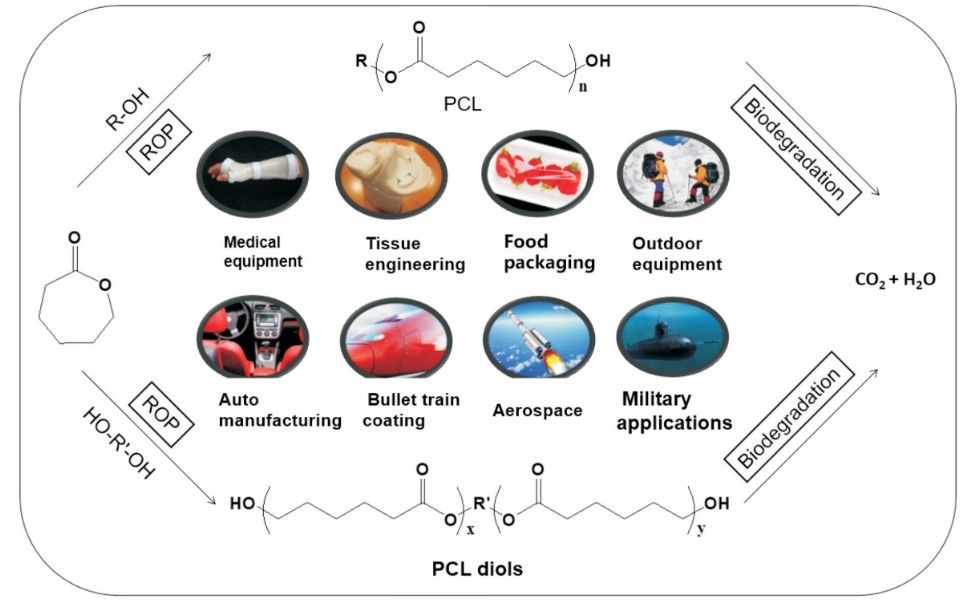 Fig. 2. Preparation and application of polymer materials with high performance (European Polymer Journal. 2022, 162: 110892).
Fig. 2. Preparation and application of polymer materials with high performance (European Polymer Journal. 2022, 162: 110892).
1,4-Butanediol (BDO) is an important organic chemical raw material. It is a saturated carbon four straight-chain diol. BDO presents different forms of colorless oily liquid or needle-like crystals depending on the temperature. As a high-volume chemical, the global market for BDO is close to 2 million tons per year, mainly for the production of different products including gamma-butanediol, tetrahydrofuran, polyurethane and polybutylene terephthalate. Therefore, BDO has a wide range of applications in the fields of medicine, automobile and chemical industry (Fig. 3).
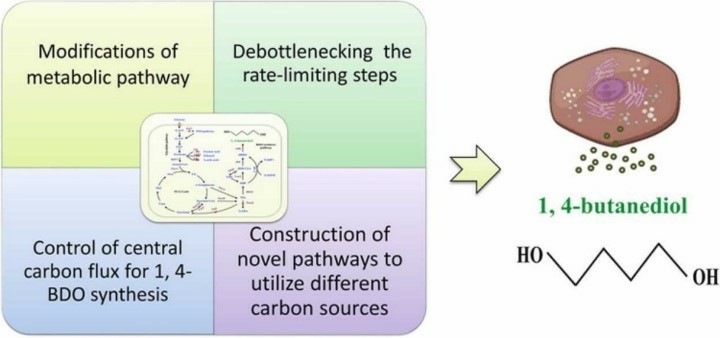 Fig. 3. Preparation and application of 1, 4-butanediol (Biochemical Engineering Journal. 2022, 185: 108478).
Fig. 3. Preparation and application of 1, 4-butanediol (Biochemical Engineering Journal. 2022, 185: 108478).
If you are interested in our biodegradable polymer monomers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Nwamba, M.C. et al. Trends and hassles in the microbial production of lactic acid from lignocellulosic biomass. Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2021, 21: 101337.
- Abdal-hay, A. et al. A review of protein adsorption and bioactivity characteristics of poly ε-caprolactone scaffolds in regenerative medicine. European Polymer Journal. 2022, 162: 110892.
- Guo, H. et al. Advances in research on the bio-production of 1,4-butanediol by the engineered microbes. Biochemical Engineering Journal. 2022, 185: 108478.


















 Fig. 1. Preparation and application of pure lactic acid (Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2021, 21: 101337).
Fig. 1. Preparation and application of pure lactic acid (Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2021, 21: 101337). Fig. 2. Preparation and application of polymer materials with high performance (European Polymer Journal. 2022, 162: 110892).
Fig. 2. Preparation and application of polymer materials with high performance (European Polymer Journal. 2022, 162: 110892). Fig. 3. Preparation and application of 1, 4-butanediol (Biochemical Engineering Journal. 2022, 185: 108478).
Fig. 3. Preparation and application of 1, 4-butanediol (Biochemical Engineering Journal. 2022, 185: 108478).












