- Molecular Weight: 302.29
- Molecular Formula: C14H14N4O4
- Molecular Weight: 214.099379685
- Molecular Formula: C14H14O2
- Molecular Weight: 224.10217365
- Molecular Formula: C8H12N6O2
- Molecular Weight: 463.92931
- Molecular Formula: C16H16Br2O6
- Molecular Weight: 302.07903816
- Molecular Formula: C16H14O6
- Molecular Weight: 376.09602564
- Molecular Formula: C23H12N4O2
- Molecular Weight: 308.177630004
- Molecular Formula: C21H24O2
- Molecular Weight: 286.09535693
- Molecular Formula: C15H14N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 588.10209467
- Molecular Formula: C31H14F6N4O2
- Molecular Weight: 454.0536467
- Molecular Formula: C18H10F4N4O6
- Molecular Weight: 500.05792605
- Molecular Formula: C28H12N4O4S
- Molecular Weight: 382.09133418
- Molecular Formula: C18H14N4O6
- Molecular Weight: 494.17427596
- Molecular Formula: C32H22N4O2
- Molecular Weight: 484.08163887
- Molecular Formula: C29H16N4S2
- Molecular Weight: 486.06090343
- Molecular Formula: C28H14N4OS2
- Molecular Weight: 270.05416083
- Molecular Formula: C16H6N4O
- Molecular Weight: 149.047678466
- Molecular Formula: C8H7NO2
- Molecular Weight: 906.39203944
- Molecular Formula: C63H54O6
- Molecular Weight: 246.01643791
- Molecular Formula: C12H6O6
- Molecular Weight: 432.11908701
- Molecular Formula: C22H20N6S2
Introduction
Polymer monomers are small molecules of synthetic polymers, which are simple compounds that can undergo polymerization or polycondensation reaction to form polymer compounds. Currently, widely used polymer monomers include the following three categories: alkenes, alcohols, carboxylic acids.

Alkenes are one of the most significant monomer compounds in the chemical industry and the main monomers for synthetic plastics. The alkene monomers represented by ethylene and styrene are widely applied in the synthesis of various plastics and occupy an important position in the field of food, medicine and cosmetics. In addition, as the most widely used alkene compounds in industrial production, ethylene and its derivatives often exist as the polymer form in daily life, such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride. As another important industrial raw material, isoprene can also be utilized in synthetic rubber, adhesives as well as in the production of vitamin A, steroids, which presents high commercial value. Furthermore, D-limonene is a monoterpene naturally present in citrus peels with specific properties that can be used in various industrial segments such as foods, perfumes and beverages.[1]
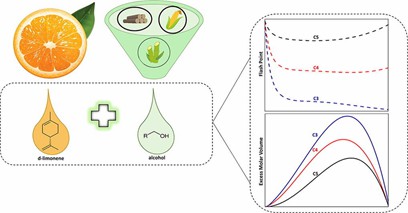 Fig. 1. Preparation and application of d-limonene (The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 2020, 150: 106224).
Fig. 1. Preparation and application of d-limonene (The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 2020, 150: 106224).
Alcohol compounds, especially polyols containing two hydroxyl groups, are important raw materials for polyester synthesis. The application of alcohol monomers in bioenergy has attracted more and more attention. In the biomass model compounds, alcohols undertake the dual roles of hydrogen donor and solvent, which provides enlightenment for realization of hydrogen-free biomass upgrading.[2] For example, N-butanol can be used as biofuels or intermediates in the production of various compounds in polymerization technology. In addition, 1,2-propanediol can also be used in in pharmaceutical intermediates, food additives. 2,3-butanediol is also an important chemical raw material for rubber and plastics.
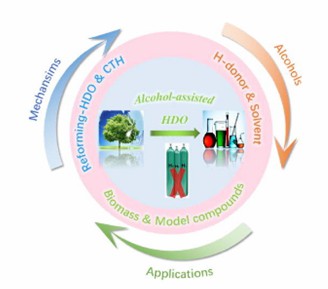 Fig. 2. Achieving H2-free biomass upgrading by polyols (Journal of Energy Chemistry. 2022, 73: 133-159).
Fig. 2. Achieving H2-free biomass upgrading by polyols (Journal of Energy Chemistry. 2022, 73: 133-159).
Carboxylic acids are important basic precursors of chemical feedstocks produced from the biotransformation of renewable feedstocks, which can be fabricated by oxidation of lignin.[3] Carboxylic acid compounds are widely used in food, medicine, cosmetics, polymer industry and other fields. In particular, hydroxyl acids and dicarboxylic acids can be applied as polymer monomers to synthesize polyester. Among them, dicarboxylic acids arean important class of high value-added chemicals, which is often used as synthetic monomers for new materials to fabricate polyester, polyamide and polyurethane. Currently, the global annual output of adipic acid, also known as fatty acid, is more than 3 million tons. Adipic acids are mainly used in the production of nylon 66, polyurethane and degradable plastic polybutylene terephthalate adipic acid ester (PBAT). In addition, polylactic acid (PLA) made from lactic acid is also an important environmentally friendly degradable material.
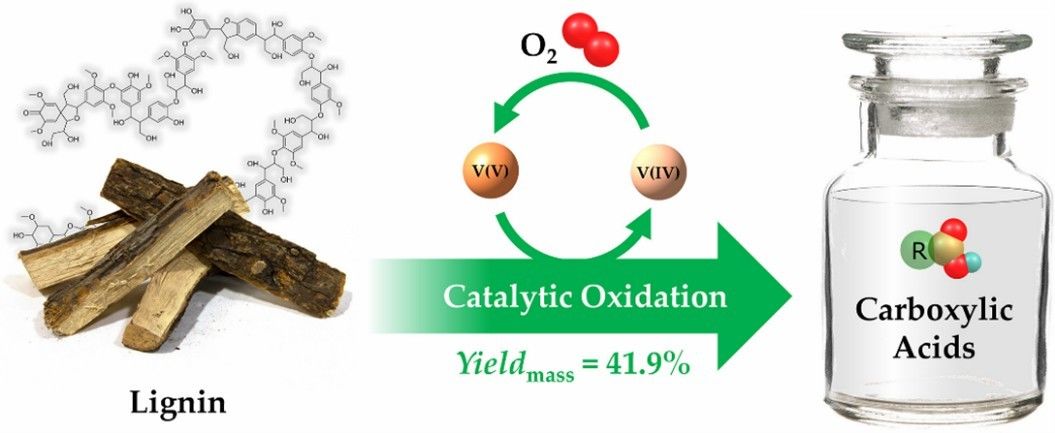 Fig. 3. Preparation of carboxylic acids (Fuel Processing Technology. 2022, 238: 107493).
Fig. 3. Preparation of carboxylic acids (Fuel Processing Technology. 2022, 238: 107493).
If you are interested in our monomers, please contact us immediately!
References
- Henriques, J.D. et al. Flash point and excess molar volumes of binary mixtures containing d-limonene and alcohol compounds from propanol to dodecanol. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 2020, 150: 106224.
- Xu, H. et al. Alcohol-assisted hydrodeoxygenation as a sustainable and cost-effective pathway for biomass derivatives upgrading. Journal of Energy Chemistry. 2022, 73: 133-159.
- Lu, T. et al. A combined experimental and theoretical study on vanadium-catalytic oxidation of lignin to produce carboxylic acids. Fuel Processing Technology. 2022, 238: 107493.







![3,3'-[(5-Methyl-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy)]diphthalonitrile](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/3-3-5-Methyl-1-3-phenylene-bis-oxy-diphthalonitrile.png)


![4,4'-[(1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2,2-propanediyl)bis(4,1-phenyleneoxy)]diphthalonitrile](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/4-4-1-1-1-3-3-3-Hexafluoro-2-2-propanediyl-bis-4-1-phenyleneoxy-diphthalonitrile.png)
![4,4'-[(2,3,5,6-Tetrafluoro-1,4-phenylene)bis(oxy)]bis(2-nitroaniline)](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/4-4-2-3-5-6-Tetrafluoro-1-4-phenylene-bis-oxy-bis-2-nitroaniline.png)
![4,4'-[(5,5-Dioxidodibenzo[b,d]thiene-2,8-diyl)bis(oxy)]diphthalonitrile](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/4-4-5-5-Dioxidodibenzo-b-d-thiene-2-8-diyl-bis-oxy-diphthalonitrile.png)
![4,4'-[1,4-Phenylenebis(oxy)]bis(2-nitroaniline)](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/4-4-1-4-Phenylenebis-oxy-bis-2-nitroaniline.png)
![4,4'-[2,2-Butanediylbis(4,1-phenyleneoxy)]diphthalonitrile](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/4-4-2-2-Butanediylbis-4-1-phenyleneoxy-diphthalonitrile.png)
![4,4'-[Methylenebis(4,1-phenylenethio)]diphthalonitrile](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/4-4-Methylenebis-4-1-phenylenethio-diphthalonitrile.png)
![4,4'-[Oxybis(4,1-phenylenethio)]diphthalonitrile](https://resource.bocsci.com/structure/4-4-Oxybis-4-1-phenylenethio-diphthalonitrile.png)


![5,5'-((5'-(4-((3-(tert-Butyl)-5-formyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)ethynyl)phenyl)-[1,1':3',1''-terphenyl]-4,4''-diyl)bis(ethyne-2,1-diyl))bis(3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde)](/images/logo.svg)



 Fig. 1. Preparation and application of d-limonene (The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 2020, 150: 106224).
Fig. 1. Preparation and application of d-limonene (The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 2020, 150: 106224). Fig. 2. Achieving H2-free biomass upgrading by polyols (Journal of Energy Chemistry. 2022, 73: 133-159).
Fig. 2. Achieving H2-free biomass upgrading by polyols (Journal of Energy Chemistry. 2022, 73: 133-159). Fig. 3. Preparation of carboxylic acids (Fuel Processing Technology. 2022, 238: 107493).
Fig. 3. Preparation of carboxylic acids (Fuel Processing Technology. 2022, 238: 107493).











